Behringer Model D Skrócona instrukcja obsługi
- Kategoria
- Klawiatury MIDI
- Typ
- Skrócona instrukcja obsługi

Quick Start Guide
MODEL D
Authentic Analog Synthesizer with 3 VCOs,
Ladder Filter, LFO and Eurorack Format
V 6.0

2 3Quick Start GuideMODEL D
Terminals marked with
this symbol carry
electrical current of
sucient magnitude to constitute risk
of electric shock. Use only high-quality
professional speaker cables with ¼" TS
or twist-locking plugs pre-installed.
Allother installation or modication
should be performed only by
qualiedpersonnel.
This symbol, wherever it
appears, alerts you to the
presence of uninsulated
dangerous voltage inside the enclosure
- voltage that may be sucient to
constitute a risk ofshock.
This symbol, wherever it
appears, alerts you to
important operating and
maintenance instructions in the
accompanying literature. Please read
themanual.
Caution
To reduce the risk of
electric shock, do not
remove the top cover (or the rear
section). No user serviceable parts inside.
Refer servicing to qualiedpersonnel.
Caution
To reduce the risk of
re or electric shock, do
not expose this appliance to rain and
moisture. Theapparatus shall not
be exposed to dripping or splashing
liquids and no objects lled with
liquids, such as vases, shall be placed
on the apparatus.
Caution
These service instructions
are for use by qualied
service personnel only. Toreduce
the risk of electric shock do not
perform any servicing other than that
contained in the operation instructions.
Repairshave to be performed by
qualied servicepersonnel.
1. Read these instructions.
2. Keep these instructions.
3. Heed all warnings.
4. Follow all instructions.
5. Do not use this apparatus
near water.
6. Clean only with dry cloth.
7. Do not block any ventilation
openings. Install in accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions.
8. Do not install near any heat
sources such as radiators, heat registers,
stoves, or other apparatus (including
ampliers) that produce heat.
9. Do not defeat the safety purpose
of the polarized or grounding-type
plug. A polarized plug has two blades
with one wider than the other.
A grounding-type plug has two blades
and a third grounding prong. The wide
blade or the third prong are provided
for your safety. Ifthe provided plug
does not t into your outlet, consult
an electrician for replacement of the
obsolete outlet.
10. Protect the power cord from being
walked on or pinched particularly
at plugs, convenience receptacles,
and the point where they exit from
the apparatus.
11. Use only attachments/accessories
specied by themanufacturer.
12. Use only with
the cart, stand,
tripod, bracket, or
table specied by
the manufacturer,
orsold with
the apparatus. When a cart is used,
use caution when moving the cart/
apparatus combination to avoid injury
from tip-over.
13. Unplug this apparatus during
lightning storms or when unused for
long periods of time.
14. Refer all servicing to qualied
service personnel. Servicing is required
when the apparatus has been damaged
in any way, such as power supply cord
or plug is damaged, liquid has been
spilled or objects have fallen into the
apparatus, the apparatus has been
exposed to rain or moisture, does not
operate normally, or has beendropped.
15. The apparatus shall be connected
to a MAINS socket outlet with a
protective earthing connection.
16. Where the MAINS plug or an
appliance coupler is used as the
disconnect device, the disconnect
device shall remain readily operable.
17. Correct disposal of
this product: This
symbol indicates that
this product must not
be disposed of with
household waste,
according to the WEEE Directive
(2012/19/EU) and your national law.
This product should be taken to a
collection center licensed for the
recycling of waste electrical and
electronic equipment (EEE).
The mishandling of this type of waste
could have a possible negative impact
on the environment and human health
due to potentially hazardous
substances that are generally
associated with EEE. At the same time,
your cooperation in the correct disposal
of this product will contribute to the
ecient use of natural resources. For
more information about where you can
take your waste equipment for
recycling, please contact your local city
oce, or your household waste
collection service.
18. Do not install in a conned space,
such as a book case or similar unit.
19. Do not place naked ame
sources, such as lighted candles,
on the apparatus.
20. Please keep the environmental
aspects of battery disposal in mind.
Batteries must be disposed-of at a
battery collection point.
21. This apparatus may be used in
tropical and moderate climates up
to 45°C.
Music Tribe accepts no liability for
any loss which may be suered by
any person who relies either wholly
or in part upon any description,
photograph, or statement contained
herein. Technical specications,
LEGAL DISCLAIMER
Important Safety
Instructions
appearances and other information
are subject to change without notice.
All trademarks are the property
of their respective owners. Midas,
Klark Teknik, Lab Gruppen, Lake,
Tannoy, Turbosound, TC Electronic,
TC Helicon, Behringer, Bugera, Aston
Microphones and Coolaudio are
trademarks or registered trademarks
of Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
© Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
2023 All rights reserved.
For the applicable warranty terms and
conditions and additional information
regarding Music Tribe’s Limited
Warranty, please see complete details
online at community.musictribe.com/
pages/support#warranty.
Las terminales marcadas
con este símbolo
transportan corriente
eléctrica de magnitud suciente como
para constituir un riesgo de descarga
eléctrica. Utilicesolo cables de altavoz
profesionales y de alta calidad con
conectores TS de 6,3 mm o de bayoneta
prejados. Cualquier otra instalación o
modicación debe ser realizada
únicamente por un técnicocualicado.
Este símbolo, siempre que
aparece, leadvierte de la
presencia de voltaje
peligroso sin aislar dentro de la caja;
estevoltaje puede ser suciente para
constituir un riesgo dedescarga.
Este símbolo, siempre que
aparece, leadvierte sobre
instrucciones operativas y
de mantenimiento que aparecen en la
documentación adjunta. Por favor,
leaelmanual.
Atención
Para reducir el riesgo de
descarga eléctrica, no
quite la tapa (olaparte posterior).
Nohay piezas en el interior del equipo
que puedan ser reparadas por el
usuario. Sies necesario, póngase en
contacto con personal cualicado.
Atención
Para reducir el riesgo
de incendio o descarga
eléctrica, no exponga este aparato a la
lluvia, humedad o alguna otra fuente
que pueda salpicar o derramar algún
líquido sobre el aparato. Nocoloque
ningún tipo de recipiente para líquidos
sobre elaparato.
Atención
Las instrucciones
de servicio deben
llevarlas a cabo exclusivamente
personal cualicado. Paraevitar el
riesgo de una descarga eléctrica,
no realice reparaciones que no se
encuentren descritas en el manual de
operaciones. Lasreparaciones deben
ser realizadas exclusivamente por
personalcualicado.
1. Lea las instrucciones.
2. Conserve estas instrucciones.
3. Preste atención a todas
las advertencias.
4. Siga todas las instrucciones.
5. No use este aparato cerca
del agua.
6. Limpie este aparato con un
paño seco.
7. No bloquee las aberturas
de ventilación. Instale el equipo
de acuerdo con las instrucciones
del fabricante.
8. No instale este equipo cerca de
fuentes de calor tales como radiadores,
acumuladores de calor, estufas u otros
aparatos (incluyendo amplicadores)
que puedan producir calor.
9. No elimine o deshabilite nunca
la conexión a tierra del aparato o del
cable de alimentación de corriente.
Unenchufe polarizado tiene dos polos,
uno de los cuales tiene un contacto
más ancho que el otro. Una clavija
con puesta a tierra dispone de tres
contactos: dos polos y la puesta a
tierra. El contacto ancho y el tercer
contacto, respectivamente, son los que
garantizan una mayor seguridad. Si el
enchufe suministrado con el equipo
no concuerda con la toma de corriente,
consulte con un electricista para
cambiar la toma de corriente obsoleta.
10. Coloque el cable de suministro de
energía de manera que no pueda ser
pisado y que esté protegido de objetos
alados. Asegúrese de que el cable de
suministro de energía esté protegido,
especialmente en la zona de la clavija y
en el punto donde sale del aparato.
11. Use únicamente los dispositivos
o accesorios especicados por
el fabricante.
12. Use
únicamente la
carretilla,
plataforma,
trípode, soporte o
mesa especicados
por el fabricante o suministrados junto
con el equipo. Altransportar el equipo,
tenga cuidado para evitar daños y
caídas al tropezar con algún obstáculo.
13. Desenchufe el equipo durante
tormentas o si no va a utilizarlo durante
un periodo largo.
14. Confíe las reparaciones
únicamente a servicios técnicos
cualicados. La unidad requiere
mantenimiento siempre que haya
sufrido algún daño, si el cable de
suministro de energía o el enchufe
presentaran daños, sehubiera
derramado un líquido o hubieran caído
objetos dentro del equipo, si el aparato
hubiera estado expuesto a la humedad
o la lluvia, si ha dejado de funcionar de
manera normal o si ha sufrido algún
golpe o caída.
15. Al conectar la unidad a la toma de
corriente eléctrica asegúrese de que
la conexión disponga de una unión
atierra.
16. Si el enchufe o conector
de red sirve como único medio
de desconexión, éste debe ser
accesiblefácilmente.
Instrucciones de
seguridad
LIMITED WARRANTY

4 5Quick Start GuideMODEL D
17. Cómo debe
deshacerse de este
aparato: Este símbolo
indica que este aparato
no debe ser tratado
como basura orgánica,
según lo indicado en la Directiva WEEE
(2012/19/EU) y a las normativas
aplicables en su país. En lugar de ello
deberá llevarlo al punto limpio más
cercano para el reciclaje de sus
elementos eléctricos/ electrónicos
(EEE). Al hacer esto estará ayudando a
prevenir las posibles consecuencias
negativas para el medio ambiente y la
salud que podrían ser provocadas por
una gestión inadecuada de este tipo de
aparatos. Además, el reciclaje de
materiales ayudará a conservar los
recursos naturales. Para más
información acerca del reciclaje de este
aparato, póngase en contacto con el
Ayuntamiento de su ciudad o con el
punto limpio local.
18. No instale esta unidad en un
espacio muy reducido, tal como
encastrada en una librería o similar.
19. No coloque objetos con
llama, como una vela encendida,
sobre este aparato.
20. Tenga presentes todas las
advertencias relativas al reciclaje
y correcta eliminación de las pilas.
Las pilas deben ser siempre eliminadas
en un punto limpio y nunca con el resto
de la basura orgánica.
21. Puede usar este aparato en
lugares con climas tropicales y
moderados que soporten temperaturas
de hasta 45°C.
Music Tribe no admite ningún tipo
de responsabilidad por cualquier
daño o pérdida que pudiera sufrir
cualquier persona por conar total
o parcialmente en la descripciones,
fotografías o armaciones
contenidas en este documento.
Las especicaciones técnicas,
imágenes y otras informaciones
contenidas en este documento están
sujetas a modicaciones sin previo
aviso. Todas las marcas comerciales
que aparecen aquí son propiedad
de sus respectivos dueños. Midas,
Klark Teknik, Lab Gruppen, Lake,
Tannoy, Turbosound, TC Electronic,
TC Helicon, Behringer, Bugera, Aston
Microphones y Coolaudio son marcas
comerciales o marcas registradas
de Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
© Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
2023 Reservados todos los derechos.
Si quiere conocer los detalles y
condiciones aplicables de la garantía
así como información adicional sobre
la Garantía limitada de Music Tribe,
consulte online toda la información en
la web community.musictribe.com/
pages/support#warranty.
Les points repérés par ce
symbole portent une
tension électrique
susante pour constituer un risque
d’électrocution. Utilisez uniquement
des câbles d’enceintes professionnels
de haute qualité avec ches Jack mono
6,35 mm ou ches à verrouillages déjà
installées. Touteautre installation ou
modication doit être eectuée
uniquement par un personnel qualié.
Ce symbole avertit de la
présence d’une tension
dangereuse et non isolée à
l’intérieur de l’appareil - elle peut
provoquer des chocs électriques.
Attention
Ce symbol signale les
consignes d’utilisation
et d’entre ! Tienimportantes dans
la documentation fournie. Lisez les
consignes de sécurité du manuel
d’utilisation del’appareil.
Attention
Pour éviter tout risque
de choc électrique,
ne pas ouvrir le capot de l’appareil
ni démonter le panneau arrière.
L’intérieur de l’appareil ne possède
aucun élément réparable par
l’utilisateur. Laissertoute réparation à
un professionnelqualié.
Attention
Pour réduire les risques
de feu et de choc
électrique, n’exposez pas cet appareil
à la pluie, à la moisissure, auxgouttes
ou aux éclaboussures. Ne posez pas
de récipient contenant un liquide sur
l’appareil (unvase par exemple).
Attention
Ces consignes de
sécurité et d’entretien
sont destinées à un personnel
qualié. Pour éviter tout risque de
choc électrique, n’eectuez aucune
réparation sur l’appareil qui ne soit
décrite par le manuel d’utilisation.
Les éventuelles réparations doivent
être eectuées uniquement par un
technicienspécialisé.
1. Lisez ces consignes.
2. Conservez ces consignes.
3. Respectez tous les avertissements.
4. Respectez toutes les
consignes d’utilisation.
5. N’utilisez jamais l’appareil à
proximité d’un liquide.
6. Nettoyez l’appareil avec un
chion sec.
7. Veillez à ne pas empêcher la
bonne ventilation de l’appareil via ses
ouïes de ventilation. Respectezles
consignes du fabricant concernant
l’installation del’appareil.
8. Ne placez pas l’appareil à
proximité d’une source de chaleur telle
qu’un chauage, une cuisinière ou
tout appareil dégageant de la chaleur
(y compris un ampli depuissance).
9. Ne supprimez jamais la sécurité
des prises bipolaires ou des prises
terre. Les prises bipolaires possèdent
deux contacts de largeur diérente.
Leplus large est le contact de sécurité.
Les prises terre possèdent deux
contacts plus une mise à la terre
servant de sécurité. Si la prise du bloc
d’alimentation ou du cordon d’ali-
mentation fourni ne correspond pas à
celles de votre installation électrique,
faites appel à un électricien pour
eectuer le changement de prise.
10. Installez le cordon d’alimentation
de telle façon que personne ne puisse
marcher dessus et qu’il soit protégé
d’arêtes coupantes. Assurez-vous
que le cordon d’alimentation est
sufsamment protégé, notamment
au niveau de sa prise électrique et
de l’endroit où il est relié à l’appareil;
cela est également valable pour une
éventuelle rallonge électrique.
11. Utilisez exclusivement
des accessoires et des appareils
supplémentaires recommandés par
lefabricant.
12. Utilisez
exclusivement des
chariots, des
diables,
desprésentoirs,
despieds et des
surfaces de travail recommandés par le
fabricant ou livrés avec le produit.
Déplacezprécautionneusement tout
chariot ou diable chargé pour éviter
d’éventuelles blessures en cas dechute.
13. Débranchez l’appareil de la
tension secteur en cas d’orage ou si
l’appareil reste inutilisé pendant une
longue période de temps.
14. Les travaux d’entretien de
l’appareil doivent être eectués
uniquement par du personnel qualié.
Aucunentretien n’est nécessaire sauf si
l’appareil est endommagé de quelque
façon que ce soit (dommagessur le
cordon d’alimentation ou la prise par
exemple), siun liquide ou un objet
a pénétré à l’intérieur du châssis, si
l’appareil a été exposé à la pluie ou
à l’humidité, s’il ne fonctionne pas
correctement ou à la suite d’une chute.
15. L’appareil doit être connecté à une
prise secteur dotée d’une protection
par mise à la terre.
16. La prise électrique ou la prise
IEC de tout appareil dénué de bouton
marche/arrêt doit rester accessible
enpermanence.
17. Mise au rebut
appropriée de ce
produit: Ce symbole
indique qu’en accord
avec la directive DEEE
(2012/19/EU) et les lois
en vigueur dans votre pays, ce produit
ne doit pas être jeté avec les déchets
ménagers. Ce produit doit être déposé
dans un point de collecte agréé pour le
recyclage des déchets d’équipements
électriques et électroniques (EEE).
Une mauvaise manipulation de ce type
de déchets pourrait avoir un impact
négatif sur l’environnement et la santé
à cause des substances potentiellement
dangereuses généralement associées à
ces équipements. En même temps,
votre coopération dans la mise au rebut
de ce produit contribuera à l’utilisation
ecace des ressources naturelles.
Pour plus d’informations sur l’endroit
où vous pouvez déposer vos déchets
d’équipements pour le recyclage,
veuillez contacter votre mairie ou votre
centre local de collecte des déchets.
18. N’installez pas l’appareil dans un
espace conné tel qu’une bibliothèque
ou meuble similaire.
19. Ne placez jamais d’objets
enammés, tels que des bougies
allumées, sur l’appareil.
20. Gardez à l’esprit l’impact
environnemental lorsque vous mettez
des piles au rebus. Les piles usées
doivent être déposées dans un point de
collecte adapté.
21. Cet appareil peut être utilisé sous
un climat tropical ou modéré avec des
températures de 45°C maximum.
Music Tribe ne peut être tenu pour
responsable pour toute perte pouvant
être subie par toute personne se
ant en partie ou en totalité à
toute description, photographie
ou armation contenue dans ce
document. Les caractéristiques,
l’apparence et d’autres informations
peuvent faire l’objet de modications
sans notication. Toutes les marques
appartiennent à leurs propriétaires
respectifs. Midas, Klark Teknik,
Lab Gruppen, Lake, Tannoy,
Turbosound, TC Electronic, TC Helicon,
Behringer, Bugera, Aston Microphones
et Coolaudio sont des marques ou
marques déposées de Music Tribe
Global Brands Ltd. © Music Tribe Global
Brands Ltd. 2023 Tous droits réservés.
Pour connaître les termes et conditions
de garantie applicables, ainsi que
les informations supplémentaires et
détaillées sur la Garantie Limitée de
Music Tribe, consultez le site Internet
community.musictribe.com/pages/
support#warranty.
Vorsicht
Die mit dem Symbol
markierten Anschlüsse
führen so viel Spannung, dassdie
Gefahr eines Stromschlags besteht.
Verwenden Sie nur hochwertige,
professionelle Lautsprecherkabel
mit vorinstallierten 6,35 mm
MONO-Klinkensteckern oder
Lautsprecherstecker mit
Drehverriegelung. Alle anderen
Installationen oder Modikationen
sollten nur von qualiziertem
Fachpersonal ausgeführt werden.
Achtung
Um eine Gefährdung
durch Stromschlag
auszuschließen, darf die
Geräteabdeckung bzw.
Geräterückwandnicht abgenommen
werden. ImInnern des Geräts benden
sich keine vom Benutzer reparierbaren
Teile. Reparaturarbeiten dürfen
nur von qualiziertem Personal
ausgeführtwerden.
Consignes de sécurité
DÉNI LÉGAL
GARANTIE LIMITÉE
Wichtige
Sicherheitshinweise
NEGACIÓN LEGAL
GARANTÍA LIMITADA

6 7Quick Start GuideMODEL D
Achtung
Um eine Gefährdung
durch Feuer bzw.
Stromschlag auszuschließen, darf
dieses Gerät weder Regen oder
Feuchtigkeit ausgesetzt werden
noch sollten Spritzwasser oder
tropfende Flüssigkeiten in das Gerät
gelangen können. Stellen Sie keine
mit Flüssigkeit gefüllten Gegenstände,
wie z. B. Vasen, aufdasGerät.
Achtung
Die Service-Hinweise sind
nur durch qualiziertes
Personal zu befolgen. Umeine
Gefährdung durch Stromschlag zu
vermeiden, führen Sie bitte keinerlei
Reparaturen an dem Gerät durch,
dienicht in der Bedienungsanleitung
beschrieben sind. Reparaturen
sind nur von qualiziertem
Fachpersonaldurchzuführen.
1. Lesen Sie diese Hinweise.
2. Bewahren Sie diese Hinweise auf.
3. Beachten Sie alle Warnhinweise.
4. Befolgen Sie alle
Bedienungshinweise.
5. Betreiben Sie das Gerät nicht in
der Nähe vonWasser.
6. Reinigen Sie das Gerät mit einem
trockenen Tuch.
7. Blockieren Sie nicht die
Belüftungsschlitze. Beachten
Sie beim Einbau des Gerätes die
Herstellerhinweise.
8. Stellen Sie das Gerät nicht in der
Nähe von Wärmequellen auf. Solche
Wärmequellen sind z. B. Heizkörper,
Herde oder andere Wärme erzeugende
Geräte (auch Verstärker).
9. Entfernen Sie in keinem Fall
die Sicherheitsvorrichtung von
Zweipol- oder geerdeten Steckern. Ein
Zweipolstecker hat zwei unterschiedlich
breite Steckkontakte. Ein geerdeter
Stecker hat zwei Steckkontakte
und einen dritten Erdungskontakt.
Derbreitere Steckkontakt oder der
zusätzliche Erdungskontakt dient
Ihrer Sicherheit. Falls das mitgelieferte
Steckerformat nicht zu Ihrer Steckdose
passt, wenden Sie sich bitte an
einen Elektriker, damit die Steckdose
entsprechend ausgetauscht wird.
10. Verlegen Sie das Netzkabel so,
dass es vor Tritten und scharfen Kanten
geschützt ist und nicht beschädigt
werden kann. Achten Sie bitte
insbesondere im Bereich der Stecker,
Verlängerungskabel und an der Stelle,
an der das Netzkabel das Gerät verlässt,
aufausreichendenSchutz.
11. Das Gerät muss jederzeit mit
intaktem Schutzleiter an das Stromnetz
angeschlossen sein.
12. Sollte der Hauptnetzstecker
oder eine Gerätesteckdose die
Funktionseinheit zum Abschalten sein,
muss diese immer zugänglich sein.
13. Verwenden Sie nur Zusatzgeräte/
Zubehörteile, dielaut Hersteller
geeignet sind.
14. Verwenden
Sie nur Wagen,
Standvorrich-
tungen, Stative,
Halter oder Tische,
die vom Hersteller
benannt oder im Lieferumfang des
Geräts enthalten sind. Falls Sie einen
Wagen benutzen, seien Sie vorsichtig
beim Bewegen der
Wagen- Gerätkombination,
umVerletzungen durch Stolpern
zuvermeiden.
15. Ziehen Sie den Netzstecker bei
Gewitter oder wenn Sie das Gerät
längere Zeit nicht benutzen.
16. Lassen Sie alle Wartungsarbeiten
nur von qualiziertem Service-
Personal ausführen. EineWartung
ist notwendig, wenn das Gerät in
irgendeiner Weise beschädigt wurde
(z. B. Beschädigung des Netzkabels
oder Steckers), Gegenstände oder
Flüssigkeit in das Geräteinnere gelangt
sind, das Gerät Regen oder Feuchtigkeit
ausgesetzt wurde, das Gerät nicht
ordnungsgemäß funktioniert oder auf
den Boden gefallen ist.
17. Korrekte
Entsorgung dieses
Produkts: Dieses Symbol
weist darauf hin, das
Produkt entsprechend
der WEEE Direktive
(2012/19/EU) und der jeweiligen
nationalen Gesetze nicht zusammen
mit Ihren Haushaltsabfällen zu
entsorgen. DiesesProdukt sollte bei
einer autorisierten Sammelstelle für
Recycling elektrischer und
elektronischer Geräte (EEE) abgegeben
werden. Wegen bedenklicher
Substanzen, diegenerell mit
elektrischen und elektronischen
Geräten in Verbindung stehen, könnte
eine unsachgemäße Behandlung dieser
Abfallart eine negative Auswirkung auf
Umwelt und Gesundheit haben.
Gleichzeitig gewährleistet Ihr Beitrag
zur richtigen Entsorgung dieses
Produkts die eektive Nutzung
natürlicher Ressourcen. Fürweitere
Informationen zur Entsorgung Ihrer
Geräte bei einer Recycling-Stelle
nehmen Sie bitte Kontakt zum
zuständigen städtischen Büro,
Entsorgungsamt oder zu Ihrem
Haushaltsabfallentsorgerauf.
18. Installieren Sie das Gerät nicht
in einer beengten Umgebung, zum
Beispiel Bücherregal oder ähnliches.
19.
Stellen Sie keine Gegenstände mit
oenen Flammen, etwa brennende
Kerzen, auf das Gerät.
20. Beachten Sie bei der Entsorgung
von Batterien den Umweltschutz-
Aspekt. Batterien müssen bei einer
Batterie-Sammelstelle entsorgt
werden.
21. Dieses Gerät ist in tropischen
und gemäßigten Klimazonen bis
45° C einsetzbar.
Music Tribe übernimmt keine Haftung
für Verluste, die Personen entstanden
sind, die sich ganz oder teilweise auf
hier enthaltene Beschreibungen,
Fotos oder Aussagen verlassen haben.
Technische Daten, Erscheinungsbild
und andere Informationen können
ohne vorherige Ankündigung geändert
werden. Alle Warenzeichen sind
Eigentum der jeweiligen Inhaber.
Midas, Klark Teknik, Lab Gruppen, Lake,
Tannoy, Turbosound, TC Electronic,
TC Helicon, Behringer, Bugera, Aston
Microphones und Coolaudio sind
Warenzeichen oder eingetragene
Warenzeichen der Music Tribe Global
Brands Ltd. © Music Tribe Global Brands
Ltd. 2023 Alle Rechte vorbehalten.
Die geltenden Garantiebedingungen
und zusätzliche Informationen
bezüglich der von Music Tribe
gewährten beschränkten
Garantie nden Sie online unter
community.musictribe.com/pages/
support#warranty.
Aviso!
Terminais marcados
com o símbolo carregam
corrente elétrica de magnitude
suciente para constituir um risco de
choque elétrico. Use apenas cabos
de alto-falantes de alta qualidade
com plugues TS de ¼" ou plugues
com trava de torção pré-instalados.
Todas as outras instalações e
modicações devem ser efetuadas por
pessoasqualicadas.
Este símbolo, onde quer
que o encontre, alerta-o
para a leitura das
instruções de manuseamento que
acompanham o equipamento. Por favor
leia o manual deinstruções.
Atenção
De forma a diminuir
o risco de choque
eléctrico, nãoremover a cobertura
(ouasecção de trás). Não existem peças
substituíveis por parte do utilizador no
seu interior. Para esse efeito recorrer a
um técnicoqualicado.
Atenção
Para reduzir o risco de
incêndios ou choques
eléctricos o aparelho não deve ser
exposto à chuva nem à humidade.
Alémdisso, não deve ser sujeito a
salpicos, nem devem ser colocados em
cima do aparelho objectos contendo
líquidos, taiscomojarras.
Atenção
Estas instruções de
operação devem ser
utilizadas, emexclusivo, por técnicos
de assistência qualicados. Para evitar
choques eléctricos não proceda a
reparações ou intervenções, que
não as indicadas nas instruções
de operação, salvo se possuir as
quali-cações necessárias. Para evitar
choques eléctricos não proceda a
reparações ou intervenções, que
não as indicadas nas instruções de
operação. Só o deverá fazer se possuir
as qualicaçõesnecessárias.
1. Leia estas instruções.
2. Guarde estas instruções.
3. Preste atenção a todos os avisos.
4. Siga todas as instruções.
5. Não utilize este dispositivo perto
de água.
6. Limpe apenas com um pano seco.
7. Não obstrua as entradas de
ventilação. Instale de acordo com as
instruções do fabricante.
8. Não instale perto de quaisquer
fontes de calor tais como radiadores,
bocas de ar quente, fogões de sala
ou outros aparelhos (incluindo
amplicadores) que produzam calor.
9. Não anule o objectivo de
segurança das chas polarizadas ou
do tipo de ligação à terra. Uma cha
polarizada dispõe de duas palhetas
sendo uma mais larga do que a outra.
Uma cha do tipo ligação à terra dispõe
de duas palhetas e um terceiro dente
de ligação à terra. A palheta larga ou
o terceiro dente são fornecidos para
sua segurança. Se a cha fornecida
não encaixar na sua tomada, consulte
um electricista para a substituição da
tomada obsoleta.
10. Proteja o cabo de alimentação de
pisadelas ou apertos, especialmente
nas chas, extensões, e no local de
saída da unidade. Certique-se de
que o cabo eléctrico está protegido.
Verique particularmente nas chas,
nos receptáculos e no ponto em que o
cabo sai doaparelho.
11. O aparelho tem de estar sempre
conectado à rede eléctrica com o
condutor de protecção intacto.
12. Se utilizar uma cha de
rede principal ou uma tomada de
aparelhos para desligar a unidade
de funcionamento, esta deve estar
sempre acessível.
13. Utilize apenas ligações/acessórios
especicados pelofabricante.
14. Utilize apenas
com o carrinho,
estrutura, tripé,
suporte, ou mesa
especicados pelo
fabricante ou
vendidos com o dispositivo.
Quandoutilizar um carrinho, tenha
cuidado ao mover o conjunto carrinho/
dispositivo para evitar danos provocados
pela terpidação.
15. Desligue este dispositivo durante
as trovoadas ou quando não for
utilizado durante longos períodos
detempo.
16. Qualquer tipo de reparação
deve ser sempre efectuado por
pessoal qualicado. É necessária uma
reparação sempre que a unidade tiver
sido de alguma forma danicada,
como por exemplo: no caso do cabo de
alimentação ou cha se encontrarem
danicados; naeventualidade de
líquido ter sido derramado ou objectos
terem caído para dentro do dispositivo;
no caso da unidade ter estado exposta
à chuva ou à humidade; seesta
não funcionar normalmente, ou se
tiver caído.
17. Correcta eliminação
deste produto: este
símbolo indica que o
produto não deve ser
eliminado juntamente
com os resíduos
domésticos, segundo a Directiva REEE
(2012/19/EU) e a legislação nacional. Este
produto deverá ser levado para um centro
de recolha licenciado para a reciclagem
de resíduos de equipamentos eléctricos e
electrónicos (EEE). O tratamento
incorrecto deste tipo de resíduos pode ter
um eventual impacto negativo no
ambiente e na saúde humana devido a
substâncias potencialmente perigosas
que estão geralmente associadas aos EEE.
Ao mesmo tempo, a sua colaboração para
a eliminação correcta deste produto irá
HAFTUNGSAUSSCHLUSS
Instruções de
Segurança Importantes
BESCHRÄNKTE GARANTIE

8 9Quick Start GuideMODEL D
contribuir para a utilização eciente dos
recursos naturais. Paramais informação
acerca dos locais onde poderá deixar o
seu equipamento usado para reciclagem,
é favor contactar os serviços municipais
locais, a entidade de gestão de resíduos
ou os serviços de recolha de
resíduosdomésticos.
18. Não instale em lugares
connados, tais como estantes ou
unidades similares.
19. Não coloque fontes de
chama, tais como velas acesas,
sobre o aparelho.
20. Favor, obedecer os aspectos
ambientais de descarte de bateria.
Baterias devem ser descartadas em um
ponto de coletas de baterias.
21. Esse aparelho pode ser usado em
climas tropicais e moderados até 45°C.
O Music Tribe não se responsabiliza
por perda alguma que possa ser
sofrida por qualquer pessoa que
dependa, seja de maneira completa
ou parcial, de qualquer descrição,
fotograa, ou declaração aqui
contidas. Dados técnicos, aparências
e outras informações estão sujeitas
a modicações sem aviso prévio.
Todas as marcas são propriedade
de seus respectivos donos. Midas,
Klark Teknik, Lab Gruppen, Lake, Tannoy,
Turbosound, TC Electronic, TC Helicon,
Behringer, Bugera
, Aston Microphones
e Coolaudio são marcas ou marcas
registradas do Music Tribe Global Brands
Ltd. © Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
2023 Todos direitos reservados.
Para obter os termos de garantia
aplicáveis e condições e informações
adicionais a respeito da garantia
limitada do Music Tribe, favor vericar
detalhes na íntegra através do website
community.musictribe.com/pages/
support#warranty.
Attenzione
I terminali contrassegnati
con il simbolo conducono
una corrente elettrica suciente a
costituire un rischio di scossa elettrica.
Usareunicamente cavi per altoparlanti
(Speaker) d’elevata qualità con
connettori jack TS da ¼"pre-installati.
Ognialtra installazione o modica deve
essere eettuata esclusivamente da
personale tecnico qualicato.
Attenzione
Questo simbolo, ovunque
appaia, avverte della
presenza di una tensione pericolosa
non isolata all'interno dello chassis,
tensione che può essere suciente per
costituire un rischio di scossa elettrica.
Attenzione
Questo simbolo,
ovunque appaia, segnala
importanti istruzioni operative e di
manutenzione nella documentazione
allegata. Si invita a leggere il manuale.
Attenzione
Per ridurre il rischio di
scosse elettriche, non
rimuovere il coperchio superiore (o la
sezione posteriore). All'interno non ci
sono parti riparabili dall'utente. Per la
manutenzione rivolgersi a personale
qualicato.
Attenzione
Per ridurre il rischio
di incendi o scosse
elettriche, non esporre questo
apparecchio a pioggia e umidità.
L'apparecchio non deve essere esposto
a gocciolio o schizzi di liquidi e nessun
oggetto contenente liquidi, come vasi,
deve essere collocato sull'apparecchio.
Attenzione
Queste istruzioni di
servizio sono destinate
esclusivamente a personale qualicato.
Per ridurre il rischio di scosse
elettriche non eseguire interventi
di manutenzione diversi da quelli
contenuti nel manuale di istruzioni. Le
riparazioni devono essere eseguite da
personale di assistenza qualicato.
1. Leggere queste istruzioni.
2. Conservare queste istruzioni.
3. Prestare attenzione a tutti gli
avvisi.
4. Applicare tutte le istruzioni.
5. Non utilizzare questo dispositivo
vicino l'acqua.
6. Pulire esclusivamente con un
panno asciutto.
7. Non bloccare le aperture di
ventilazione. Installare in conformità
con le istruzioni del produttore.
8. Non installare vicino a fonti di
calore come radiatori, termoregolatori,
stufe o altri apparecchi (inclusi
amplicatori) che producono calore.
9. Non escludere la sicurezza fornita
dalla spina polarizzata o con messa
a terra. Una spina polarizzata ha due
lame, una più larga dell'altra. Una spina
con messa a terra ha due lame e un
terzo polo di messa a terra. La lama
larga o il terzo polo sono forniti per
la vostra sicurezza. Se la spina fornita
non si adatta alla presa, consultare un
elettricista per la sostituzione della
presa obsoleta.
10. Proteggere il cavo di
alimentazione dal calpestio o essere
schiacciato in particolare alle spine,
prese di corrente e il punto in cui esce
dall'apparecchio.
11. Utilizzare esclusivamente
dispositivi/accessori specicati dal
produttore.
GARANTIA LIMITADA
LEGAL RENUNCIANTE
12. Utilizzare
solo carrelli,
supporti, treppiedi,
stae o tavoli
indicati dal
produttore o
venduti con l'apparecchio. Utilizzando
un carrello, prestare attenzione quando
si sposta la combinazione carrello/
apparecchio per evitare lesioni dovute
al ribaltamento.
13. Scollegare questo apparecchio
durante i temporali o se non è utilizzato
per lunghi periodi di tempo.
14. Per tutte le riparazioni rivolgersi a
personale qualicato. La manutenzione
è necessaria quando l'apparecchio
è danneggiato in qualsiasi modo,
come danneggiamento del cavo
di alimentazione o della spina,
versamento di liquido o oggetti caduti
nell'apparecchio, se l'apparecchio è
stato esposto a pioggia o umidità, se
non funziona normalmente o è caduto.
15. L'apparecchio deve essere
collegato a una presa di corrente
elettrica con messa a terra di
protezione.
16. e la spina o una presa del
dispositivo è utilizzata come dispositivo
di disconnessione, deve essere
facilmente utilizzabile.
17. Smaltimento
corretto di questo
prodotto: questo
simbolo indica che
questo dispositivo non
deve essere smaltito
insieme ai riuti domestici, secondo la
Direttiva RAEE (2012/19 / UE) e la vostra
legislazione nazionale. Questo prodotto
deve essere portato in un centro di
raccolta autorizzato per il riciclaggio di
riuti di apparecchiature elettriche ed
elettroniche (RAEE). La cattiva gestione
di questo tipo di riuti potrebbe avere
un possibile impatto negativo
sull'ambiente e sulla salute umana a
causa di sostanze potenzialmente
pericolose che sono generalmente
associate alle apparecchiature
elettriche ed elettroniche. Nello stesso
tempo la vostra collaborazione al
corretto smaltimento di questo
prodotto contribuirà all'utilizzo
eciente delle risorse naturali. Per
ulteriori informazioni su dove è
possibile trasportare le apparecchiature
per il riciclaggio vi invitiamo a
contattare l'ucio comunale locale o il
servizio di raccolta dei riuti domestici.
18. Non installare in uno spazio
ristretto, come in una libreria o in una
struttura simile.
19. Non collocare sul dispositivo fonti
di amme libere, come candele accese.
20. Per lo smaltimento delle batterie,
tenere in considerazione gli aspetti
ambientali. Le batterie devono essere
smaltite in un punto di raccolta delle
batterie esauste.
21. Questo apparecchio può essere
usato in climi tropicali e temperati
no a 45°C.
Music Tribe non si assume alcuna
responsabilità per eventuali danni
che possono essere subiti da chiunque
si adi in tutto o in parte a qualsiasi
descrizione, fotograa o dichiarazione
contenuta qui. Speciche tecniche,
aspetti e altre informazioni sono
soggette a modiche senza preavviso.
Tutti i marchi sono di proprietà
dei rispettivi titolari. Midas, Klark
Teknik, Lab Gruppen, Lake, Tannoy,
Turbosound, TC Electronic, TC Helicon,
Behringer, Bugera, Aston Microphones
e Coolaudio sono marchi o marchi
registrati di Music Tribe Global Brands
Ltd. © Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
2023 Tutti i diritti riservati.
Per i termini e le condizioni di garanzia
applicabili e le informazioni aggiuntive
relative alla garanzia limitata di Music
Tribe, consultare online i dettagli
completi su community.musictribe.
com/pages/support#warranty.
Waarschuwing
Aansluitingen die gemerkt
zijn met het symbool
voeren een zodanig hoge spanning dat
ze een risico vormen voor elektrische
schokken. Gebruikuitsluitend
kwalitatief hoogwaardige, in de
handel verkrijgbare luidsprekerkabels
die voorzien zijn van ¼"TS stekkers.
Laatuitsluitend gekwaliceerd
personeel alleoverige installatie- of
modicatiehandelingenuitvoeren.
Dit symbool wijst u altijd
op belangrijke bedienings
- en
onderhoudsvoorschriften in de
bijbehorende documenten. Wijvragen
u dringend de handleiding te lezen.
Attentie
Verwijder in geen
geval de bovenste
afdekking (vanhet achterste gedeelte)
anders bestaat er gevaar voor een
elektrische schok. Hetapparaat bevat
geen te onderhouden onderdelen.
Reparatiewerkzaamheden mogen
uitsluitend door gekwaliceerd
personeel uitgevoerdworden.
Attentie
Om het risico op brand
of elektrische schokken
te beperken, dient u te voorkomen
dat dit apparaat wordt blootgesteld
aan regen en vocht. Hetapparaat
mag niet worden blootgesteld aan
neerdruppelend of opspattend water
en er mogen geen met water gevulde
voorwerpen – zoals een vaas – op het
apparaat wordengezet.
Attentie
Deze
onderhoudsinstructies
zijn uitsluitend bedoeld voor
gekwaliceerd onderhoudspersoneel.
Omelektrische schokken te
voorkomen, mag u geen andere
DISCLAIMER LEGALE
GARANZIA LIMITATA
Informazioni importanti
Belangrijke
veiligheidsvoorschriften

10 11Quick Start GuideMODEL D
onderhoudshandelingen verrichten dan
in de bedieningsinstructies vermeld
staan. Reparatiewerkzaamheden
mogen alleen uitgevoerd worden door
gekwaliceerd onderhoudspersoneel.
1. Lees deze voorschriften.
2. Bewaar deze voorschriften.
3. Neem alle waarschuwingen
in acht.
4. Volg alle voorschriften op.
5. Gebruik dit apparaat niet in de
buurt vanwater.
6. Reinig het uitsluitend met een
drogedoek.
7. Let erop geen van de ventilatie-
openingen te bedekken. Plaats en
installeer het volgens de voor- schriften
van de fabrikant.
8. Het apparaat mag niet worden
geplaatst in de buurt van radiatoren,
warmte-uitlaten, kachels of andere
zaken (ook versterkers) diewarmte
afgeven.
9. Maak de veiligheid waarin door
de polarisatie- of aardingsstekker
wordt voorzien, niet ongedaan.
Eenpolarisatiestekker heeft twee
bladen, waarvaner een breder is dan
het andere. Een aardingsstekker heeft
twee bladen en een derde uitsteeksel
voor de aarding. Het bredere blad of
het derde uitsteeksel zijn er voor uw
veiligheid. Mochtde geleverde stekker
niet in uw stopcontact passen, laat
het contact dan door een elektricien
vervangen.
10. Om beschadiging te voorkomen,
moetde stroomleiding zo gelegd
worden dat er niet kan worden over
gelopen en dat ze beschermd is
tegen scherpe kanten. Zorg zeker
voor voldoende bescherming aan de
stekkers, deverlengkabels en het punt
waar het netsnoer het apparaat verlaat.
11. Het toestel met altijd met een
intacte aarddraad aan het stroomnet
aangeslotenzijn.
12. Wanneer de stekker
van het hoofdnetwerk of een
apparaatstopcontact de functionele
eenheid voor het uitschakelen is,
dientdeze altijd toegankelijk te zijn.
13. Gebruik uitsluitend door de
producent gespeci- ceerd toebehoren
c.q. onderdelen.
14. Gebruik
het apparaat
uitsluitend in
combinatie met de
wagen, hetstatief,
dedriepoot, de
beugel of tafel die door de producent
is aangegeven, of die in combinatie
met het apparaat wordt verkocht. Bij
gebruik van een wagen dient men
voorzichtig te zijn bij het verrijden van
de combinatie wagen/apparaat en
letsel door vallen tevoorkomen.
15. Bij onweer en als u het apparaat
langere tijd niet gebruikt, haalt u de
stekker uit hetstopcontact.
16. Laat alle voorkomende reparaties
door vakkundig en bevoegd personeel
uitvoeren. Reparatiewerk-zaamheden
zijn nodig als het toestel op enige wijze
beschadigd is geraakt, bijvoorbeeld
als de hoofd-stroomkabel of -stekker
is beschadigd, als er vloeistof of
voorwerpen in terecht zijn gekomen,
als het aan regen of vochtigheid
heeft bloot-gestaan, niet normaal
functioneert of wanneer het
isgevallen.
17. Correcte afvoer van
dit product: dit symbool
geeft aan dat u dit
product op grond van de
AEEA-richtlijn
(2012/19/EU) en de
nationale wetgeving van uw land niet
met het gewone huishoudelijke afval
mag weggooien. Dit product moet na
aoop van de nuttige levensduur naar
een ociële inzamelpost voor
afgedankte elektrische en elektronische
apparatuur (AEEA) worden gebracht,
zodat het kan worden gerecycleerd.
Vanwegede potentieel gevaarlijke
stoen die in elektrische en
elektronische apparatuur kunnen
voorkomen, kaneen onjuiste afvoer van
afval van het onderhavige type een
negatieve invloed op het milieu en de
menselijke gezondheid hebben.
Eenjuiste afvoer van dit product is
echter niet alleen beter voor het milieu
en de gezondheid, maardraagt tevens
bij aan een doelmatiger gebruik van de
natuurlijke hulpbronnen. Voormeer
informatie over de plaatsen waar u uw
afgedankte apparatuur kunt inleveren,
kunt u contact opnemen met uw
gemeente of de
plaatselijkereinigingsdienst.
18. Installeer niet in een kleine
ruimte, zoals een boekenkast of iets
dergelijks.
19. Plaats geen open vlammen, zoals
brandende kaarsen, op het apparaat.
20. Houd rekening met de
milieuaspecten van het afvoeren van
batterijen. Batterijen moeten bij een
inzamelpunt voor batterijen worden
ingeleverd.
21. Dit apparaat kan worden gebruikt
in tropische en gematigde klimaten
tot 45 ° C.
Music Tribe aanvaardt geen
aansprakelijkheid voor enig verlies
dat kan worden geleden door een
persoon die geheel of gedeeltelijk
vertrouwt op enige beschrijving,
foto of verklaring hierin. Technische
specicaties, verschijningen en
andere informatie kunnen zonder
voorafgaande kennisgeving worden
gewijzigd. Alle handelsmerken zijn
eigendom van hun respectievelijke
eigenaren. Midas, Klark Teknik, Lab
Gruppen, Lake, Tannoy, Turbosound,
TC Electronic, TC Helicon, Behringer,
Bugera, Aston Microphones en
Coolaudio zijn handelsmerken of
gedeponeerde handelsmerken
van Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
© Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
2023 Alle rechten voorbehouden.
Voor de toepasselijke
garantievoorwaarden en aanvullende
informatie met betrekking tot de
beperkte garantie van Music Tribe,
zie de volledige details online op
community.musictribe.com/pages/
support#warranty.
WETTELIJKE ONTKENNING
Varning
Uttag markerade med
symbolen leder elektrisk
strömstyrka som är tillräckligt stark för
att utgöra en risk för elchock. Använd
endast högkvalitativa, kommersiellt
tillgängliga högtalarkablar med
förhandsinstallerade ¼"TS-
kontakter. Allannan installering eller
modikation bör endast utföras av
kompetentpersonal.
Den här symbolen
hänvisar till viktiga
punkter om användning
och underhåll i den medfölljande
dokumentationen. Varvänlig och läs
bruksanvisningen.
Försiktighet
Minska risken för
elektriska stötar genom
att aldrig ta av höljet upptill på
apparaten (ellerta av baksidan).
Inuti apparaten nns det inga delar
som kan repareras av användaren.
Endastkvalicerad personal får
genomföra reparationer.
Försiktighet
För att minska risken
för brand och elektriska
stötar ska apparaten skyddas mot
regn och fukt. Apparaten går inte
utsättas för dropp eller spill och
inga vattenbehållare som vaser etc.
fårplaceras på den.
Försiktighet
Serviceinstruktionen
är enbart avsedd
för kvalicerad servicepersonal.
Föratt undvika risker genom
elektriska stötar, genomför inga
reparationer på apparaten, vilka inte
är beskrivna i bruksanvisningen.
Endast kvalicerad fackpersonal får
genomförareparationerna.
1. Läs dessa anvisningar.
2. Spara dessa anvisningar.
3. Beakta alla varningar.
4. Följ alla anvisningar.
5. Använd inte apparaten i närheten
av vatten.
6. Rengör endast med torr trasa.
7. Blockera inte
ventilationsöppningarna.
Installeraenligt tillverkarens
anvisningar.
8. Installera aldrig intill värmekällor
som värme- element, varmluftsintag,
spisareller annan utrustning som avger
värme (inklusiveförstärkare).
9. Ändra aldrig en polariserad
eller jordad kontakt. Enpolariserad
kontakt har två blad – det ena bredare
än det andra. En jordad kontakt har
två blad och ett tredje jordstift. Det
breda bladet eller jordstiftet är till för
din säkerhet. Omden medföljande
kontakten inte passar i ditt uttag,
skadu kontakta en elektriker för att få
uttaget bytt.
10. Förlägg elkabeln så, att det inte
är möjligt att trampa på den och att
den är skyddad mot skarpa kanter och
inte kan skadas. Ge i synnerhet akt på
områdena omkring stickkontakterna,
förlängningskablarna och på det
ställe, där elkabeln lämnar apparaten,
ärtillräckligtskyddade.
11. Apparaten måste alltid
vara ansluten till elnätet med
intaktskyddsledare.
12. Om huvudkontakten, ellerett
apparatuttag, fungerar som
avstängningsenhet måste denna alltid
varatillgänglig.
13. Använd endast tillkopplingar och
tillbehör som angetts av tillverkaren.
14. Använd
endast med vagn,
stativ, trefot,
hållareeller bord
som angetts
av tillverkaren,
ellersom sålts till-sammans med
apparaten. Om du använder en
vagn, var försiktig, när du föryttar
kombinationen vagn-apparat, för att
förhindra olycksfall genomsnubbling.
15. Dra ur anslutningskontakten und
åskväder eller när apparaten inte ska
användas under någon längre tid.
16. Låt kvalicerad personal utföra
all service. Serviceär nödvändig
när apparaten har skadats, t.ex.när
en elkabel eller kontakt är skadad,
vätskaeller främmande föremål har
kommit in i apparaten, eller när den har
fallit i golvet.
17. Kassera produkten
på rätt sätt: den här
symbolen indikerar att
produkten inte ska
kastas i
hushållssoporna,
enligtWEEE direktivet (2012/19/EU)
ochgällande, nationell lagstiftning.
Produkten ska lämnas till ett
auktoriserat återvinningsställe för
elektronisk och elektrisk utrustning
(EEE). Om den här sortens avfall
hanteras på fel sätt kan miljön, och
människors hälsa, påverkas negativt på
grund av potentiella risksubstanser
som ofta associeras med EEE.
Avfallshanteras produkten däremot på
rätt sätt bidrar detta till att naturens
resurser används på ett bra sätt.
Kontakta kommun, ansvarig
förvaltning eller
avfallshanteringsföretag för mer
information om återvinningscentral
där produkten kanlämnas.
18. Installera inte i ett trångt
utrymme, t.ex. i en bokhylsa eller
liknande enhet.
19.
Placera inte källor med öppen eld,
t.ex. tända ljus, på apparaten.
20. Tänk på miljöaspekterna
vid kassering av batterier.
Batterier måste kasseras på ett
batteriuppsamlingsställe.
21. Denna apparat kan användas
i tropiska och måttliga klimat
upp till 45 ° C.
Viktiga
säkerhetsanvisningar
BEPERKTE GARANTIE

12 13Quick Start GuideMODEL D
Music Tribe tar inget ansvar för någon
förlust som kan drabbas av någon
person som helt eller delvis förlitar
sig på någon beskrivning, fotogra
eller uttalande som nns här.
Tekniska specikationer, utseenden
och annan information kan ändras
utan föregående meddelande. Alla
varumärken tillhör respektive ägare.
Midas, Klark Teknik, Lab Gruppen,
Lake, Tannoy, Turbosound, TC
Electronic, TC Helicon, Behringer,
Bugera, Aston Microphones och
Coolaudio är varumärken eller
registrerade varumärken som tillhör
Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
© Music Tribe Global Brands Ltd.
2023 Alla Rättigheter reserverade.
För tillämpliga garantivillkor och
ytterligare information om Music
Tribes begränsade garanti, se
fullständig information online på
community.musictribe.com/pages/
support#warranty.
Uwaga
Terminale oznaczone
symbolem przenoszą
wystarczająco wysokie napięcie
elektryczne, aby stworzyć ryzyko
porażenia prądem. Używaj
wyłącznie wysokiej jakości
fabrycznie przygotowanych kabli
z zainstalowanymi wtyczkami
¼"TS. Wszystkie inne instalacje lub
modykacje powinny być wykonywane
wyłącznie przez wykwalikowany
personel techniczny.
Ten symbol informuje o
ważnych wskazówkach
dotyczących obsługi i
konserwacji urządzenia w dołączonej
dokumentacji. Proszę przeczytać
stosowne informacje w instrukcji
obsługi.
Uwaga
W celu wyeliminowania
zagrożenia porażenia
prądem zabrania się zdejmowania
obudowy lub tylnej ścianki urządzenia.
Elementyznajdujące się we wnętrzu
urządzenia nie mogą być naprawiane
przez użytkownika. Naprawymogą
być wykonywane jedynie przez
wykwalikowanypersonel.
Uwaga
W celu wyeliminowania
zagrożenia porażenia
prądem lub zapalenia się urządzenia
nie wolno wystawiać go na działanie
deszczu i wilgotności oraz dopuszczać
do tego, aby do wnętrza dostała się
woda lub inna ciecz. Nie należy stawiać
na urządzeniu napełnionych cieczą
przedmiotów takich jak np. wazony lub
szklanki.
Uwaga
Prace serwisowe mogą
być wykonywane jedynie
przez wykwalikowany personel.
Wcelu uniknięcia zagrożenia porażenia
prądem nie należy wykonywać
żadnych manipulacji, które nie
są opisane w instrukcji obsługi.
Naprawywykonywane mogą być
jedynie przez wykwalikowany
personeltechniczny.
1. Proszę przeczytać
poniższewskazówki.
2. Proszę przechowywać
niniejsząinstrukcję.
3. Należy przestrzegać wszystkich
wskazówek ostrzegawczych.
4. Należy postępować zgodnie z
instrukcjąobsługi.
5. Urządzenia nie wolno używać w
pobliżuwody.
6. Urządzenie można czyścić
wyłącznie suchąszmatką.
7. Nie zasłaniać otworów
wentylacyjnych. Wczasie podłączania
urządzenia należy przestrzegać
zaleceńproducenta.
8. Nie stawiać urządzenia w pobliżu
źródeł ciepła takich, jak grzejniki,
piecelub urządzenia produkujące
ciepło (np.wzmacniacze).
9. W żadnym wypadku nie należy
usuwać zabezpieczeń z wtyczek
dwubiegunowych oraz wtyczek z
uziemieniem. Wtyczka dwubiegunowa
posiada dwa wtyki kontaktowe o różnej
szerokości. Wtyczkaz uziemieniem ma
dwa wtyki kontaktowe i trzeci wtyk
uziemienia. Szerszy wtyk kontaktowy
lub dodatkowy wtyk uziemienia służą
do zapewnienia bezpieczeństwa
użytkownikowi. Jeśli format wtyczki
urządzenia nie odpowiada standardowi
gniazdka, proszę zwrócić się do
elektryka z prośbą o wymienienie
gniazda.
10. Kabel sieciowy należy ułożyć
tak, aby nie był narażony na deptanie i
działanie ostrych krawędzi, co mogłoby
doprowadzić do jego uszkodzenia.
Szczególną uwagę zwrócić należy na
odpowiednią ochronę miejsc w pobliżu
wtyczek i przedłużaczy oraz miejsce,
wktórym kabel sieciowy przymocowany
jest dourządzenia.
11. Urządzenie musi być zawsze
podłączone do sieci sprawnym
przewodem z uziemieniem.
12. Jeżeli wtyk sieciowy lub gniazdo
sieciowe w urządzeniu pełnią funkcję
wyłącznika, tomuszą one być zawsze
łatwodostępne.
13. Używać wyłącznie sprzętu
dodatkowego i akcesoriów zgodnie z
zaleceniami producenta.
14. Używać
jedynie zalecanych
przez producenta
lub znajdujących
się w zestawie
wózków,
stojaków, statywów, uchwytów i
stołów. Wprzypadku posługiwania
się wózkiem należy zachować
szczególną ostrożność w trakcie
przewożenia zestawu, abyuniknąć
niebezpieczeństwa potknięcia się i
zranienia.
15. W trakcie burzy oraz na
czas dłuższego nieużywania
urządzenia należy wyjąć wtyczkę z
gniazdkasieciowego.
16. Wykonywanie wszelkich
napraw należy zlecać jedynie
wykwalikowanym pracownikom
serwisu. Przeprowadzenie przeglądu
technicznego staje się konieczne, jeśli
urządzenie zostało uszkodzone w
jakikolwiek sposób (dotyczy to także
kabla sieciowego lub wtyczki), jeśli
do wnętrza urządzenia dostały się
przedmioty lub ciecz, jeśli urządzenie
wystawione było na działanie deszczu
lub wilgoci, jeśli urządzenie nie
funkcjonuje poprawnie oraz kiedy
spadło napodłogę.
17. Prawidłowa
utylizacja produktu:
Tensymbol wskazuje,
żetego produktu nie
należy wyrzucać razem
ze zwykłymi odpadami
domowymi, tylko zgodnie z dyrektywą
w sprawie zużytego sprzętu
elektrycznego i elektronicznego
(WEEE) (2012/19/EU) oraz przepisami
krajowymi. Niniejszy produkt należy
przekazać do autoryzowanego punktu
zbiórki zużytego sprzętu elektrycznego
i elektronicznego. Niewłaściwe
postępowanie z tego typu odpadami
może wywołać szkodliwe działanie na
środowisko naturalnej i zdrowie
człowieka z powodu potencjalnych
substancji niebezpiecznych zaliczanych
jako zużyty sprzęt elektryczny i
elektroniczny. Jednocześnie, Twój
wkład w prawidłową utylizację
niniejszego produktu przyczynia się do
oszczędnego wykorzystywania
zasobów naturalnych. Szczegółowych
informacji o miejscach, w których
można oddawać zużyty sprzęt do
recyklingu, udzielają urzędy miejskie,
przedsiębiorstwa utylizacji odpadów
lub najbliższy zakład utylizacji
odpadów.
18. Nie instaluj w ograniczonej
przestrzeni, takiej jak półka na książki
lub podobny zestaw.
19. Nie stawiaj na urządzeniu źródeł
otwartego ognia, takich jak zapalone
świece.
20. Należy pamiętać o
środowiskowych aspektach utylizacji
baterii. Baterie należy utylizować w
punkcie zbiórki baterii.
21. To urządzenie może być
używane w klimacie tropikalnym i
umiarkowanym do 45 ° C.
Music Tribe nie ponosi
odpowiedzialności za jakiekolwiek
straty, które mogą ponieść osoby,
które polegają w całości lub w
części na jakimkolwiek opisie,
fotograi lub oświadczeniu
zawartym w niniejszym dokumencie.
Specykacje techniczne, wygląd i
inne informacje mogą ulec zmianie
bez powiadomienia. Wszystkie
znaki towarowe są własnością ich
odpowiednich właścicieli. Midas,
Klark Teknik, Lab Gruppen, Lake,
Tannoy, Turbosound, TC Electronic,
TC Helicon, Behringer, Bugera, Aston
Microphones i Coolaudio są znakami
towarowymi lub zastrzeżonymi
znakami towarowymi rmy Music
Tribe Global Brands Ltd. © Music Tribe
Global Brands Ltd. 2023 Wszystkie
prawa zastrzeżone.
Aby zapoznać się z obowiązującymi
warunkami gwarancji i dodatkowymi
informacjami dotyczącymi
ograniczonej gwarancji Music Tribe,
zapoznaj się ze wszystkimi szczegółami
w trybie online pod adresem
community.musictribe.com/pages/
support#warranty.
ZASTRZEŻENIA PRAWNE
ZASTRZEŻENIA PRAWNE
BEGRÄNSAD GARANTI
FRISKRIVNINGSKLAUSUL Ważne informacje o
bezpieczeństwie
OGRANICZONA GWARANCJA

14 15Quick Start GuideMODEL D
(EN) Step 1: Hook-Up
(ES) Paso 1: Conexión
(FR) Etape 1 : Connexions
(DE) Schritt 1: Verkabelung
(PT) Passo 1: Conexões
(IT) Passo 1: Allacciare
(NL) Stap 1: Aansluiten
(SE) Steg 1: Anslutning
(PL) Krok 1: Podłączeni
MODEL D Hook-up
Desktop Computer
MIDI Keyboard
Headphones
Studio Monitors
Audio Interface
USB B
MIDI IN
MIDI OUT
USB B
USB A
USB A
Power
Adaptor
(EN) Studio System
(ES) Sistema para estudio de grabación
(FR) Système de studio
(DE) Studio-System
(PT) Sistema de Estúdio
(IT) Studio System
(NL) Studio-systeem
(SE) Studio-systemet
(PL) Studio System

16 17Quick Start GuideMODEL D
MODEL D Hook-up
Headphones
Power
Adaptor
Expression Pedal
Footswitch
MIDI Keyboard
MIDI OUT
MIDI IN
Keyboard Amplier
(EN) Band / Practice System
(ES) Sistema para un grupo/ensayos
(FR) Système pour répétition
(DE) Band/Proberaum-System
(PT) Sistema Banda/Prática
(IT) Sistema band / pratica
(NL) Band / oefensysteem
(SE) Band / övningssystem
(PL) Zespół / system ćwiczeń
(EN) Step 1: Hook-Up
(ES) Paso 1: Conexión
(FR) Etape 1 : Connexions
(DE) Schritt 1: Verkabelung
(PT) Passo 1: Conexões
(IT) Passo 1: Allacciare
(NL) Stap 1: Aansluiten
(SE) Steg 1: Anslutning
(PL) Krok 1: Podłączeni

18 19Quick Start GuideMODEL D
(EN) Live System
(ES) Sistema para actuación en directo
(FR) Système pour représentation
(DE) Live-System
(PT) Sistema Ao Vivo
(IT) Sistema live
(NL) Live-systeem
(SE) Live-system
(PL) System na żywo
Expression Pedal
Footswitch
Headphones
Power
Adaptor
MIDI Keyboard
MIDI OUT
Mixing console
Active Loudspeakers
Laptop Computer
USB B
USB A
MIDI IN
MODEL D Hook-up
(EN) Step 1: Hook-Up
(ES) Paso 1: Conexión
(FR) Etape 1 : Connexions
(DE) Schritt 1: Verkabelung
(PT) Passo 1: Conexões
(IT) Passo 1: Allacciare
(NL) Stap 1: Aansluiten
(SE) Steg 1: Anslutning
(PL) Krok 1: Podłączeni

20 21Quick Start GuideMODEL D
MODEL D Hook-up
(EN) Step 1: Hook-Up
(ES) Paso 1: Conexión
(FR) Etape 1 : Connexions
(DE) Schritt 1: Verkabelung
(PT) Passo 1: Conexões
(IT) Passo 1: Allacciare
(NL) Stap 1: Aansluiten
(SE) Steg 1: Anslutning
(PL) Krok 1: Podłączeni
(EN) Poly Chain System
(ES) Sistema de cadena de polietileno
(FR) Système de chaîne poly
(DE) Poly Chain System
(PT) Poly Chain System
(IT) Sistema Poly Chain
(NL) Poly Chain-systeem
(SE) Poly kedjesystem
(PL) Poly Chain System
MIDI IN MIDI THRU MIDI IN MIDI THRU MIDI IN MIDI THRU
To next MODEL D
From next MODEL D
MIDI Keyboard
MIDI OUT
Mixing console
Active Loudspeakers
Headphones

22 23Quick Start GuideMODEL D
MODEL D Controls
(1)
(6) (7)
(36) (47)
(46)
(35)
(34)
(8)
(9)
(5)
(33)
(32) (44)
(42)
(45)
(43)
(31)
(30)
(4)
(2) (3) (17)
(10) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) (20) (21) (22)
(24)
(25)
(23)
(18) (26) (27)
(37) (38) (39) (40) (41) (48) (49)
(28) (29)(19)
(51)(50)
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
(52) (53)

24 25Quick Start GuideMODEL D
(EN) Step 2: Controls
MIDI Section
(1) USB PORT – This USB type B jack
allows connection to a computer.
The MODEL D will show up as a
class-compliant USB MIDI device,
capable of supporting MIDI in
and out.
USB MIDI IN – accepts incoming
MIDI data from an application.
USB MIDI OUT – sends MIDI data
to an application.
(2) MIDI IN – this 5-pin DIN
jack receives MIDI data from
an external source. This will
commonly be a MIDI keyboard,
an external hardware sequencer,
a computer equipped with a MIDI
interface, etc.
(3) MIDI THRU – this 5-pin DIN jack
is used to pass through MIDI
data received at the MIDI INPUT.
This will commonly be sent to
another MODEL D synthesizer
to run a Poly Chain or to a drum
machine assigned to a dierent
MIDI Channel.
Controllers Section
(4) OSC3/FILTER EG – switch
between OSC 3 or the Filter
Envelope as a modulation source.
(5) GLIDE – adjust the amount of
Glide (Portamento), between
notes on the keyboard.
(6) TUNE – adjust the frequency of
oscillators 1, 2, and 3. (OSC3 is
not aected if the OSC3 CONTROL
switch is o.)
(7) OSCILLATOR MODULATION –
when ON, the three oscillators are
modulated by the modulation mix,
set by the MOD MIX knob.
(8) MOD MIX – adjust the modulation
mix between OSC3/Filter EG and
Noise/LFO.
(9) NOISE (MOD SRC)/ LFO – switch
between Noise (or external
modulation source) or Low
Frequency Oscillator (LFO)
as a modulation source.
(10) MOD DEPTH – adjust the
modulation depth from o
to maximum. The modulation
depth can also be adjusted using
the modulation wheel
on a MIDI keyboard.
(11) WAVE SHAPE – select the LFO
wave shape from either triangular
or square wave.
(12) LFO RATE – adjusts the frequency
of the LFO.
Oscillator Bank Section
(13) OSC 3 CONTROL – when ON, the
frequency of Oscillator 3 will vary
with the keyboard. When OFF,
the keyboard, Pitch wheel, and
Modulation wheel, will have no
eect on OSC3.
(14) FREQUENCY RANGE – select from
six frequency ranges of Oscillator
1, 2, or 3.
(15) FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENT –
adjust the frequency of Oscillator
2 or 3.
(16) WAVE SHAPE – select the wave
shape used for Oscillator 1, 2, or
3 from: triangular, triangular/
sawtooth (OSC 1 and 2), reverse
sawtooth (OSC 3), sawtooth,
square, medium pulse,
and narrow pulse.
(17) MOD SOURCE (INPUT) – a
llows connection of an external
modulation source. If nothing is
connected here, then the internal
Noise generator is available as a
modulation source.
(18) OSC 1V/OCT (INPUT) – this input
allows the frequency of the three
oscillators to be adjusted by an
external control voltage (1 Volt
input increase, will increase the
frequency by one Octave).
(19) LFO CV (INPUT) – allows control
of the LFO frequency by an
external control voltage.
Mixer Section
(20) VOLUME – adjust the volume
of Oscillator 1, 2, or 3.
(21) ON/OFF – select the sources to
play from OSC 1, OSC 2, OSC 3,
Noise, and External Input, or any
combination of these 5 sources.
(22) NOISE VOLUME – adjust the level
of the internal Noise source.
(23) WHITE/PINK – switch the internal
Noise source from Pink noise to
White noise.
(24) OVERLOAD – indicates when
the audio levels of the mix are
overloading the mixer section.
(25) EXT IN VOLUME – adjust the level
of any external source playing into
the external Input. If nothing is
connected to the external input,
then instead of any external audio
coming in at this point, the main
MODEL D output is automatically
connected here.
This creates a feedback path from
the output back into the mixer
section, to get extra phat bass or
extra crunch. In this case, the EXT
IN volume control will adjust the
level of the incoming main audio
fed back into the mixer section.
(26) LFO Triangular (OUTPUT)
– outputs the internal LFO
triangular-wave signal.
(27) LFO Square (OUTPUT) –
outputs the internal LFO
square-wave signal.
(28) EXT (INPUT) – connect any
external line-level audio source
to this 3.5 mm input. If nothing
is connected here, then the
main audio output is internally
connected to this external input.
(29) MIX (OUTPUT) – outputs the nal
mix from this Mixer section.
Modiers Section
(30) DECAY – when ON, the signal
will decay during the time set
by the DECAY TIME knob after
a note or external trigger is
released. When OFF, it will decay
immediately after a note or
external trigger is released.
LOUDNESS DECAY – aects
the decay of volume level of the
Loudness section.
FILTER DECAY – aects the decay
of the cuto frequency of the
Filter section.
(31) KEYBOARD CONTROL – these
switches vary the eect of the
keyboard tracking, where the lter
section is aected by the pitch of
note played.
Switch 1 and 2 OFF –
no keyboard tracking eect
Switch 1 and 2 ON –
maximum eect
Switch 1 ON (only) –
⁄ of maximum eect
Switch 2 ON (only) –
⁄ of maximum eect
(32) FILTER MODULATION –
when ON, the lter section is
modulated by the modulation mix,
set by the MOD MIX knob.
(33) FILTER MODE – select the lter
between Low-pass or High-pass.
(34) LOUDNESS CONTOUR – these
3 knobs adjust the overall shape
enveloping the audio after it has
passed through the mixer section
and lter section. The controls
aect the change in volume
(loudness) level with time.
ATTACK – adjust the time it takes
for the signal to reach a maximum
level after a note is played.
DECAY TIME – adjust the time
for a signal to decay down to
the sustain volume level after
the attack time is over. If the
LOUDNESS DECAY switch is ON, this
is also how long it takes to decay to
minimum once a note is released.
SUSTAIN – adjust the volume level
that the signal is sustained after
the attack time and initial decay
time have been reached.
(35) FILTER ENVELOPE CONTROLS –
these 3 knobs adjust the overall
shape enveloping the lter
section. The controls aect
the change in cuto frequency
with time.
ATTACK – adjust the time for
the cuto frequency to increase
from its set value and reach the
frequency set by the AMOUNT OF
CONTOUR control.
DECAY TIME – adjust the time
for the cuto frequency to decay
down to the sustain frequency
after the attack time is over. If the
FILTER DECAY switch is ON, then
this decay time is also how long
it takes to decay from the sustain
frequency once a note is released.
SUSTAIN – adjust the cuto to a
frequency which is sustained after
the attack time and initial decay
time have been reached.
(36) FILTER CONTROLS – the lter
can be low-pass or high-pass,
depending on the setting of the
FILTER MODE switch. In low-pass
mode, audio frequencies above the
cuto frequency
are attenuated. In high-pass
mode, audio frequencies
below the cuto frequency
are attenuated.
CUTOFF FREQUENCY – adjusts
the cut-o frequency of the lter.
FILTER EMPHASIS – adjusts
the amount of volume level
boost (resonance) given at the
cut-o frequency.
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR – adjusts
the amount of frequency shift
given to the cuto frequency.
(37) CUT CV (INPUT) – allows
connection of a control voltage to
control the cuto frequency.
(38) FC GATE (INPUT) – allows an
external trigger voltage to be
applied to trigger the lter contour.
(39) FILT CONT (OUTPUT) – outputs
the lter contour.
(40) LC GATE (INPUT) – allows
an external trigger voltage
to be applied to trigger the
loudness contour.
(41) LOUD CONTOUR (OUTPUT) –
outputs the loudness contour.
Output Section
(42) A-440 – use this to turn on an
output tuning signal of 440 Hz
concert pitch. This switch can also
be used to enter various modes
during turn-on (see the Getting
Started section of this manual for
more details).
(43) POWER – this LED shows
when power is applied and the
synthesizer is turned on.
(44) VOLUME – adjust the
overall volume level of the
synthesizer output.
(45) VOLUME (HEADPHONE) – adjust
the overall volume level of the
PHONES output.
(46) PHONES – connect your
headphones to this 3.5 mm
TRS output. Make sure the
headphone volume is turned down
before putting on headphones.
(47) ON – use this to quickly turn on
or Mute the main audio output
of the synthesizer.
(48) LOUD CV (INPUT) – allows
connection of an external
control voltage to control the
Loudness Contour.
(49) MAIN (OUTPUT) – use this 3.5
mm TRS connection to output
the main audio output. Typically
it is patched to an audio input of
the MODEL D or the audio inputs
of other modular synthesizer
equipment. If you are using the
MODEL D in a Eurorack, then this is
the main output, as the rear panel
output connectors are not used.
Rear Panel
(50) MAIN OUTPUT – connect these
¼" TRS outputs to the inputs
of your external equipment as
follows (note that they are both
Mono, and not left/right):
LOW – this instrument-level
mono output can connect to the
instrument-level inputs of guitar
ampliers or mixers for example.
HIGH – this line-level mono
output can connect to the line-
level inputs of mixers, keyboard
ampliers, or powered speakers
for example.
(51) MIDI CHANNEL – these 4 switches
allow you to set the MIDI Channel
number from 1 to 16 (see the table
on page 15). The MIDI channel
can also be changed using MIDI
SysEx commands, as shown in
the MIDI SysEx tables later in
this manual. (This method is used
when the MODEL D is housed in a
Eurorack, and these switches are
no longer present.)
(52) POWER – turn the synthesizer
on or o. Make sure all the
connections are made before
turning on the unit.
(53) DC INPUT – connect the supplied
12V DC power adapter here.
The power adapter can be plugged
into an AC outlet capable of
supplying from 100V to 240V at
50 Hz/60 Hz. Use only the power
adapter supplied.
MODEL D Controls

26 27Quick Start GuideMODEL D
(ES) Paso 2: Controles
Sección MIDI
(1) USB PORT – esta toma USB de
tipo B permite la conexión a
un ordenador. El MODEL D aparece
como un dispositivo MIDI USB
class-compliant, capaz de admitir
entrada y salida MIDI.
USB MIDI IN – admite los datos
MIDI entrantes procedentes de
una aplicación.
USB MIDI OUT – da salida a datos
MIDI a una aplicación.
(2) MIDI IN – esta toma DIN de 5
puntas recibe los datos MIDI
procedentes de una fuente
exterior. Esta fuente será
habitualmente un teclado MIDI,
un secuenciador externo, un
ordenador equipado con un
interface MIDI, etc.
(3) MIDI THRU – esta toma DIN de
5 puntas se usa para re-enviar
los datos MIDI recibidos a través
de MIDI INPUT. Normalmente
conectará esta toma a otro
sintetizador MODEL D para usar
una cadena polifónica (Poly Chain)
o a una caja de ritmos asignada a
otro canal MIDI.
Sección de controladores
(4) OSC3/FILTER EG – le permite
conmutar entre OSC3 o la
envolvente de ltro como una
fuente de modulación.
(5) GLIDE – esto ajusta la cantidad
de ligadura o Glide (Portamento),
entre notas del teclado.
(6) TUNE – esto ajusta la frecuencia
de los osciladores 1, 2 y 3. (OSC3
no se ve afectado si el interruptor
OSC3 CONTROL está en OFF).
(7) OSCILLATOR MODULATION –
cuando esté en la posición ON, los
tres osciladores serán modulados
por la mezcla de modulación,
ajustada con el mando MOD MIX.
(8) MOD MIX – este mando ajusta la
mezcla de modulación entre OSC3/
Filter EG y Noise/LFO.
(9) NOISE (MOD SRC)/ LFO –
le permite conmutar entre ruido
(o una fuente de modulación
externa) o un oscilador de baja
frecuencia (LFO) como una fuente
de modulación.
(10) MOD DEPTH – este mando
ajusta la profundidad de
modulación entre o y máximo.
Esta profundidad de modulación
también puede ser ajustada por
medio de la rueda de modulación
de un teclado MIDI.
(11) WAVE SHAPE – este interruptor le
permite elegir la forma de la onda
LFO entre triangular y cuadrada.
(12) LFO RATE – este mando ajusta la
frecuencia del LFO.
Sección de banco
de oscilador
(13) OSC 3 CONTROL – cuando
este interruptor esté en ON,
la frecuencia de OSC 3 variará con
el teclado. Cuando esté en OFF,
el teclado, la rueda de inexión
tonal y la rueda de modulación no
tendrán efecto sobre OSC 3.
(14) FREQUENCY RANGE – este
selector le permite elegir entre seis
posibles rangos de frecuencia para
el oscilador 1, 2 ó 3.
(15) FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENT –
este mando le permite ajustar la
frecuencia del oscilador 2 ó 3.
(16) WAVE SHAPE – este selector
le permite elegir la forma de la
onda del oscilador 1, 2 ó 3 entre:
triangular, triangular/ diente
de sierra (OSC1 y 2), diente de
sierra invertido (OSC3), diente de
sierra, cuadrada, pulso medio y
pulso estrecho.
(17) MOD SOURCE (ENTRADA) –
permite la conexión de una
fuente de modulación externa.
Si no conecta aquí nada,
entonces tendrá disponible el
generador de ruido interno como
fuente de modulación.
(18) OSC 1V/OCT (ENTRADA) –
esta entrada le permite ajustar la
frecuencia de los tres osciladores
con un control de voltaje externo
(el aumento de la entrada en
1 voltio hará que la frecuencia
aumente en una octava).
(19) LFO CV (ENTRADA) – le permite el
control de la frecuencia del LFO por
un control de voltaje externo.
Sección de mezclador
(20) VOLUME – este mando le permite
ajustar el volumen del oscilador
1, 2 ó 3.
(21) ON/OFF – este interruptor le
permite elegir las fuentes a
reproducir entre OSC1, OSC2,
OSC3, ruido y entrada externa,
o cualquier combinación posible
entre esas 5 fuentes.
(22) NOISE VOLUME – este mando
ajusta el nivel de la fuente de
ruido interna.
(23) WHITE/PINK – este interruptor
le permite conmutar la fuente de
ruido interna entre ruido rosa y
ruido blanco.
(24) OVERLOAD – este piloto le indica
en qué momento los niveles audio
de la mezcla están saturando la
sección de mezclador.
(25) EXT IN VOLUME – ajusta el nivel
de la señal de reproducción de
cualquier fuente externa recibida
a través de la entrada externa.
Si no hay nada conectado a la
entrada externa, en lugar de esa
señal audio externa recibida en
este punto, automáticamente será
conectada aquí la salida principal
del MODEL D.
Esto crea una ruta de
realimentación desde la salida de
vuelta a la sección de mezclador
para ofrecerle un extra de graves
o un mayor sonido crunch. En
este caso, el control de volumen
EXT IN ajusta el nivel de la señal
audio principal entrante que es
enviada de nuevo a la sección de
mezclador.
(26) LFO Triangular (SALIDA) – esta
toma emite la señal de onda
triangular del LFO interno.
(27) LFO Square (SALIDA) – esta toma
emite la señal de onda cuadrada
del LFO interno.
(28) EXT (ENTRADA) – conecte en
esta toma de 3,5 mm cualquier
fuente audio de nivel de línea
externa. Si no conecta nada aquí,
entonces la salida audio será
conectada internamente a esta
entrada externa.
(29) MIX (SALIDA) – esta toma da
salida a la mezcla nal de esta
sección de mezclador.
Sección de modicadores
(30) DECAY – cuando este interruptor
esté en ON, la señal decaerá
durante el tiempo ajustado con
el mando DECAY TIME una vez
que deje de pulsar una nota o
disparador externo. Cuando
esté en OFF la señal decaerá de
forma inmediata (se cortará)
una vez que libere la nota o el
disparador externo.
LOUDNESS DECAY – esto afecta al
decaimiento del nivel de volumen
de la sección Loudness o de
volumen percibido.
FILTER DECAY – esto afecta al
decaimiento de la frecuencia de
corte de la sección de ltro.
(31) KEYBOARD CONTROL – estos
interruptores modican el efecto
del control o seguimiento de
teclado, en el que la sección de
ltro se ve afectado por el tono de
la nota tocada.
Interruptor 1 y 2 OFF – no hay
efecto de seguimiento de teclado
Interruptor 1 y 2 ON –
efecto máximo
Interruptor 1 ON (solo) – ⁄ del
efecto máximo
Interruptor 2 ON (solo) – ⁄ del
efecto máximo
(32) FILTER MODULATION – cuando
este interruptor esté ajustado
a ON, la sección de ltro será
modulada por la mezcla de
modulación, ajustada con el
mando MOD MIX.
(33) FILTER MODE – este interruptor
le permite conmutar el ltro entre
pasabajos o pasa-altos.
(34) LOUDNESS CONTOUR – estos
3 mandos ajustan la forma de
la envolvente global del audio
una vez que pasa a través de la
sección de mezclador y la de ltro.
Estos controles afectan al cambio
en el nivel de volumen (volumen
percibido) con respecto al tiempo.
ATTACK – este mando ajusta el
tiempo que tarda la señal en llegar
al nivel máximo una vez que la
nota es tocada.
DECAY TIME – este mando ajusta
el tiempo que tarda la señal
en decaer o llegar al nivel de
volumen de sustain una vez que ha
pasado el tiempo de ataque. Si el
interruptor LOUDNESS DECAY está
en la posición ON, esto también
será el tiempo que tardará la señal
en decaer al mínimo una vez que
deje de pulsar la nota.
SUSTAIN – esto ajusta el nivel
de volumen al que es mantenida
la señal después del tiempo
de ataque y una vez que ha
sido alcanzado el tiempo de
decaimiento inicial.
(35) FILTER ENVELOPE CONTROLS –
estos 3 mandos ajustan la forma
global que modela la sección de
ltro. Los controles afectan al
cambio de la frecuencia de corte a
lo largo del tiempo.
ATTACK – esto ajusta el tiempo
que debe pasar para que la
frecuencia de corte aumente desde
su valor ajustado hasta el valor de
frecuencia ajustado con el control
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR.
DECAY TIME – esto ajusta el
tiempo que tarda la frecuencia de
corte en decaer hasta la frecuencia
de sostenido o sustain una vez
que ha transcurrido el tiempo
de ataque. Si el interruptor FILTER
DECAY está en ON, entonces este
tiempo de decaimiento también
será lo que tarda en decaer desde
la frecuencia de sustain una vez
que haya dejado de pulsar la nota.
SUSTAIN – esto ajusta el corte
para una frecuencia mantenida
una vez que ha pasado el tiempo
de ataque y el de decaimiento
inicial.
(36) FILTER CONTROLS – el ltro
puede ser pasabajos o pasa-
altos, dependiendo del ajuste
del interruptor FILTER MODE.
En el modo pasabajos, las
frecuencias audio que estén por
encima de la frecuencia de corte
serán atenuadas. En el modo
pasa-altos, serán atenuadas
las frecuencias audio que estén
por debajo de la frecuencia de
corte ajustada.
CUTOFF FREQUENCY – esto ajusta
la frecuencia de corte del ltro.
FILTER EMPHASIS – esto le
permite ajustar la cantidad
de realce de nivel de volumen
(resonancia) aplicado en la
frecuencia de corte.
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR –
le permite ajustar la cantidad de
cambio de frecuencia aplicada en
la frecuencia de corte.
(37) CUT CV (ENTRADA) – le permite la
conexión de un control de voltaje
para el control de la frecuencia
de corte.
(38) FC GATE (ENTRADA) – le permite
aplicar un disparador de voltaje
externo para controlar el contorno
o modelado del ltro.
(39) FILT CONT (SALIDA) – da salida al
modelado de ltro.
(40) LC GATE (ENTRADA) – le permite
aplicar un disparador de voltaje
externo para controlar el contorno
o modelado de volumen percibido.
(41) LOUD CONTOUR (SALIDA) –
da salida al modelado de
volumen percibido.
Sección de salida
(42) A-440 – use este interruptor
para activar la emisión de una
señal de anación clásica de
440 Hz. También puede usar este
interruptor para activar distintos
modos durante el proceso de
arranque (para más detalles vea
la sección de Puesta en marcha de
este manual).
(43) POWER – este piloto se
ilumina cuando el sintetizador
está encendido.
(44) VOLUME – este control le permite
ajustar el nivel de volumen global
de la salida del sintetizador.
(45) VOLUME (HEADPHONE) – esto
ajusta el nivel de volumen global
de la salida de auriculares PHONES.

28 29Quick Start GuideMODEL D
(46) PHONES – conecte a esta salida
TRS de 3,5 mm unos auriculares.
Asegúrese de que el volumen
de salida de auriculares esté al
mínimo antes de ponérselos en
sus oídos.
(47) ON – use este interruptor para
activar rápidamente o desactivar
(mute) la salida audio principal
del sintetizador.
(48) LOUD CV (ENTRADA) – permite
la conexión de un control de
voltaje externo con el que
controlar el modelado del volumen
percibido (también conocido
como loudness).
(49) MAIN (SALIDA) – use esta
toma en TRS de 3,5 mm para la
emisión de la señal de salida audio
principal. Habitualmente esto es
cableado a una entrada audio del
MODEL D o a las entradas audio de
otros sintetizadores modulares.
Si está usando el MODEL D en
bastidor Eurorack, entonces esta
será la salida principal, dado que
los conectores de salida del panel
trasero no son usados.
Panel trasero
(50) MAIN OUTPUT – conecte
estas tomas de salida en TRS
de 6,3 mm a las entradas de su
dispositivo externo de la forma
siguiente (tenga en cuenta
que ambas salidas son mono,
no izquierda/derecha):
LOW – puede conectar esta salida
mono con nivel de instrumento
a las entradas de nivel de
instrumento de amplicadores
de guitarra o mezcladores,
por ejemplo.
HIGH – esta salida mono con
nivel de línea puede ser conectada
a las entradas de nivel de línea
de mezcladores, amplicadores
de teclado o altavoces
autoamplicados, por ejemplo.
(51) MIDI CHANNEL – estos 4
interruptores de posición le
permite ajustar el número de
canal MIDI entre el 1 y el 16
(vea la tabla de la página 15).
El canal MIDI también puede
ser modicado usando órdenes
SysEx (sistema operativo)
MIDI, tal como puede ver en las
tablas SysEx MIDI más adelante.
(Este método se usa cuando el
MODEL D esté instalado en un
Eurorack y estos interruptores ya
no están presentes.)
(52) POWER – esto le permite
encender y apagar el sintetizador.
Antes de encender esta unidad,
asegúrese de que estén hechas
todas las conexiones y que el
volumen esté al mínimo.
(53) DC INPUT – conecte aquí el
adaptador de corriente de
12 V incluido. Puede conectar
este adaptador de corriente a una
salida de corriente alterna con
un voltaje de entre 100 y 240 V
y un amperaje de 50 Hz/60 Hz.
Utilice únicamente el adaptador
de corriente incluido.
(ES) Paso 2: Controles (FR) Etape 2 : Réglages
Section MIDI
(1) USB PORT – ce port USB de
type B permet la connexion à
un ordinateur. Le MODEL D est
un appareil USB MIDI reconnu
nativement et capable de gérer
les messages MIDI entrants et
sortants.
ENTRÉE USB MIDI – accepte les
données MIDI entrantes provenant
d’une application.
SORTIE USB MIDI – permet
d’envoyer des données MIDI
à une application.
(2) MIDI IN – ce connecteur DIN à 5
broches permet de recevoir des
données MIDI depuis une source
externe. Il s’agit en général d’un
clavier MIDI, d’un séquenceur
hardware externe, d’un ordinateur
équipé d’une interface MIDI, etc.
(3) MIDI THRU – ce connecteur DIN
à 5 broches permet de transférer
les données MIDI reçues à l’entrée
MIDI IN. Il est généralement
utilisé avec un autre synthétiseur
MODEL D pour créer une chaine
polyphonique ou avec une
boite à rythmes assignées à un
autre canal.
Section Controllers
(4) OSC3/FILTER EG – permet
de sélectionner l’OSC3 ou
l’enveloppe du ltre comme source
de modulation.
(5) GLIDE – permet de régler le
glissement (Portamento) entre les
notes du clavier.
(6) TUNE – permet de régler la
fréquence des oscillateurs 1, 2 et 3
(n’agit pas sur l’OSC3 si le réglage
OSC3 CONTROL n’est pas activé).
(7) OSCILLATOR MODULATION –
lorsque cette fonction est activée,
les trois oscillateurs sont modulés
par le mixage de modulation établi
par le potentiomètre MOD MIX.
(8) MOD MIX – permet de régler
le mixage de modulation entre
les fonctions OSC3/Filter EG et
Noise/LFO.
(9) NOISE (MOD SRC)/ LFO – permet
de sélectionner le générateur de
bruit interne (ou une source de
modulation externe) ou le LFO
(Low Frequency Oscillator) comme
source de modulation.
(10) MOD DEPTH – permet de régler
l’intensité de la modulation, de 0
à sa valeur maximale. L’intensité
de la modulation peut également
être contrôlée par la molette de
modulation d’un clavier MIDI.
(11) WAVE SHAPE – permet de
sélectionner la forme de l’onde
du LFO: triangulaire ou carrée.
(12) LFO RATE – permet de régler la
fréquence du LFO.
Section Oscillator Bank
(13) OSC 3 CONTROL – lorsque cette
fonction est activée, la fréquence
de l’OSC 3 varie avec le clavier.
Lorsqu’elle est désactivée, le
clavier et les molettes de Pitch et
de modulation n’ont pas d’eet
sur l’OSC 3.
(14) FREQUENCY RANGE – permet de
sélectionner l’une des six plages
de fréquences pour l’oscillateur
1, 2 ou 3.
(15) FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENT –
permet de régler la fréquences de
l’oscillateur 2 ou 3.
(16) WAVE SHAPE – permet de
sélectionner la forme d’onde de
l’oscillateur 1, 2, ou 3 parmi les
formes suivantes : triangulaire,
triangulaire/dent de scie (OSC1
et 2), dent de scie inversée
(OSC3), dent de scie, carrée,
impulsionnelle moyenne et
impulsionnelle courte.
(17) MOD SOURCE (ENTRÉE) – permet
de connecter une source de
modulation externe. Si aucune
source n’est connectée à cette
entrée, c’est le générateur de
bruit interne qui est utilisé comme
source de modulation.
(18) OSC 1V/OCT (ENTRÉE) – cette
entrée permet de contrôler la
fréquence des trois oscillateurs
avec une tension de contrôle
externe (une augmentation
d’1 Volt en entrée permet
d’augmenter la fréquence
d’une octave).
(19) LFO CV (ENTRÉE) – permet
de contrôler la fréquence du
LFO à l’aide d’une tension de
contrôle externe.
Section Mixer
(20) VOLUME – permet de régler le
volume de l’oscillateur 1, 2 ou 3.
(21) ON/OFF – permettent de
sélectionner les sources sonores
utilisées : OSC1, OSC2, OSC3,
générateur de bruit et source
externe, ou toute combinaison de
ces 5 sources.
(22) NOISE VOLUME – permet de
régler le volume du générateur
interne de bruit.
(23) WHITE/PINK – permet de
sélectionner le type de bruit
généré: bruit rose (Pink) ou
blanc (White).
(24) OVERLOAD – ce témoin s’allume si
les niveaux sonores font saturer la
section de mixage.
(25) EXT IN VOLUME – permet de
régler le niveau d’une source
externe connectée à l’entrée
External Input. Si aucune
connexion n’est eectuée
à cette entrée, la sortie
principale du MODEL y est alors
automatiquement connectée.
Cela permet de créer un retour
depuis la sortie directement dans
la section de mixage et d’obtenir
des basses particulièrement
grasses ou un son plus énergique.
Dans ce cas, le réglage de volume
EXT IN permet d’ajuster le niveau
du signal principal retourné dans
dans la section de mixage.

30 31Quick Start GuideMODEL D
(FR) Etape 2 : Réglages
(26) LFO Triangular – porte le
signal de l’onde triangulaire
du LFO interne.
(27) LFO Square – porte le signal de
l’onde carrée du LFO interne.
(28) EXT (ENTRÉE) – vous pouvez
connecter toute source sonore
externe de niveau ligne à cette
entrée MiniJack 3,5 mm. Si aucune
connexion n’est eectuée à cette
embase, elle porte le signal de
sortie principal.
(29) MIX (SORTIE) – porte le mixage
nal de la section Mixer.
Section Modiers
(30) DECAY – lorsque cette fonction
est activée, le signal diminue
progressivement en fonction de la
durée établie par le réglage DECAY
TIME lorsqu’une touche ou qu’un
déclencheur externe est relâché. Si
la fonction est désactivée, le signal
disparait immédiatement après
le relâchement de la touche ou du
déclencheur externe.
LOUDNESS DECAY – agit sur
le Decay du volume de la
section Loudness.
FILTER DECAY – agit sur le Decay
de la fréquence de coupure du
ltre (section Filter).
(31) KEYBOARD CONTROL – ces
interrupteurs permettent de faire
varier l’eet du traçage du clavier
qui agit sur le ltre en fonction de
la hauteur de la note jouée.
Interrupteurs 1 et 2 sur OFF –
le traçage du clavier est désactivé
Interrupteurs 1 et 2 sur ON –
l’eet agit au maximum
Interrupteur 1 (uniquement)
sur ON – ⁄ de l’eet maximal
Interrupteur 2 (uniquement)
sur ON – ⁄ de l’eet maximal
(32) FILTER MODULATION – lorsque
cette fonction est activée,
le ltre est modulé par le mixage
de modulation établi par le
potentiomètre MOD MIX.
(33) FILTER MODE – permet de
sélectionner le type de ltre:
passe-bas ou passe-haut.
(34) LOUDNESS CONTOUR – ces 3
potentiomètres permettent de
régler l’enveloppe du signal audio
après qu’il ait traversé les sections
Mixer et Filter. Les réglages
agissent sur le volume du signal en
fonction du temps.
ATTACK – Permet de régler
le temps nécessaire pour que
le signal atteigne son niveau
maximum après qu’une note
soit jouée.
DECAY TIME – Permet de régler
le temps nécessaire pour que
le niveau du signal diminue
jusqu’au niveau de maintient une
fois le temps d’attaque terminé.
Si la fonction LOUD DECAY est
activée, ce potentiomètre permet
également de régler le temps
nécessaire pour que le signal
atteigne son niveau minimum une
fois la note relâchée.
SUSTAIN – permet de régler le
niveau de maintien du signal une
fois le temps d’attaque et la durée
du Decay terminés.
(35) FILTER ENVELOPE CONTROLS –
ces 3 potentiomètres permettent
de régler la forme de l’enveloppe
du ltre. Les réglages agissent
sur la fréquence de coupure en
fonction du temps.
ATTACK – permet de régler le
temps nécessaire pour que la
fréquence de coupure augmente
depuis sa valeur initiale jusqu’à la
valeur établie par le potentiomètre
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR.
DECAY TIME – permet de régler
le temps nécessaire pour que la
valeur de la fréquence de coupure
diminue jusqu’au niveau établie
par le réglage Sustain une fois
le temps d’attaque terminé.
Si la fonction FILTER DECAY est
activée, ce potentiomètre permet
également de régler le temps
nécessaire pour que la fréquence
de coupure atteigne sa valeur
minimale une fois la note relâchée.
SUSTAIN – permet de régler la
valeur de la fréquence de coupure
qui est maintenue une fois le
temps d’attaque et la durée du
Decay terminés.
(36) FILTER CONTROLS – le ltre
peut fonctionner en passe-bas
ou passe-haut en fonction du
réglage du sélecteur FILTER
MODE. En mode Lo (passe-bas),
les fréquences supérieures à
la fréquence de coupure sont
atténuées. En mode Hi (passe-
haut), les fréquences inférieures
à la fréquence de coupure
sont atténuées.
CUTOFF FREQUENCY – permet
de régler la fréquence de coupure
du ltre.
FILTER EMPHASIS – permet de
régler la quantité d’amplication
du volume (résonance) appliquée à
la fréquence de coupure.
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR – permet
de régler la variation appliquée à
la fréquence de coupure.
(37) CUT CV (ENTRÉE) – permet
de connecter une tension de
contrôle pour régler la fréquence
de coupure.
(38) FC GATE (ENTRÉE) – permet
d’utiliser une tension externe pour
déclencher le contour du ltre.
(39) FILT CONT (SORTIE) – sortie du
contour du ltre.
(40) LC GATE (ENTRÉE) – permet
d’utiliser une tension externe pour
déclencher le contour du volume.
(41) LOUD CONTOUR – sortie du
contour du volume.
Section Output
(42) A-440 – cet interrupteur permet
de générer un signal de référence
à 440 Hz. Il permet également de
placer l’appareil dans diérents
modes durant la phase de mise
sous tension (voir la section Mise
en Œuvre de ce mode d’emploi
pour plus de détails).
(43) POWER – cette LED s’allume
lorsque le synthétiseur est
sous tension.
(44) VOLUME – réglage du
volume général.
(45) VOLUME (CASQUE) – réglage
du volume général de la
sortie PHONES.
(46) PHONES – connectez un casque
audio à cette sortie MiniJack stéréo
3,5 mm. Assurez que le volume de
cette sortie est au minimum avant
de connecter votre casque.
(47) ON – utilisez cet interrupteur pour
activer ou couper rapidement
la sortie audio principale
du synthétiseur.
(48) LOUD CV (ENTRÉE) – permet de
connecter une tension de contrôle
externe pour régler le contour
du volume.
(49) MAIN (SORTIE) – cette sortie
MiniJack 3,5 mm symétrique
porte le signal de sortie principal.
Elle est généralement connectée
à une entrée audio d’un MODEL
D ou d’autres synthétiseurs
modulaires. Si votre MODEL D est
monté en rack, cette sortie fait
oce de sortie principale et les
connecteurs de la face arrière ne
sont pas utilisés.
Face arrière
(50) MAIN OUTPUT – connectez ces
sorties Jack symétriques 6,35mm
aux entrées de votre équipement
externe comme indiqué ci-dessous
(Remarque : ces sorties sont toutes
les deux mono et ne portent pas le
signal gauche ou droite):
LOW – cette sortie mono niveau
instrument peut être connectée,
par exemple, à l’entrée d’un ampli
pour guitare ou d’une console
de mixage.
HIGH – cette sortie mono niveau
ligne peut être connectée, par
exemple, à l’entrée niveau ligne
d’une console de mixage, à
un ampli pour clavier ou à des
enceintes actives.
(51) MIDI CHANNEL – ces 4 sélecteurs
vous permettent de congurer
le canal MIDI de 1 à 16 (voir le
tableau page 15). Vous pouvez
également modier le canal
MIDI en utilisant une commande
MIDI SysEx, comme indiqué
dans le tableau MIDI SysEx que
vous trouverez dans les pages
suivantes de ce mode d’emploi.
(Cette méthode est utilisée si
le MODEL D est monté dans un
Eurorack et que ces interrupteurs
ne sont plus accessibles.)
(52) POWER – permet de mettre le
synthétiseur sous/hors tension.
Assurez-vous d’avoir eectué
toutes les connexions et que le
volume est au minimum avant de
mettre l’appareil sous tension.
(53) DC INPUT – connectez
l’adaptateur secteur 12V fourni
à cette embase. Vous pouvez
brancher l’adaptateur à une prise
secteur délivrant un courant
alternatif de 100V à 240V à 50
Hz/60 Hz. Utilisez uniquement
l’adaptateur fourni.

32 33Quick Start GuideMODEL D
(DE) Schritt 2: Bedienelemente
MIDI-Sektion
(1) USB PORT – Über diesen
USB Typ B-Port kann man
einen Computer anschließen.
Der MODEL D wird als
standardkonformes USB
MIDI-Gerät angezeigt, das MIDI In
und Out unterstützt.
USB MIDI IN – Akzeptiert
eingehende MIDI-Daten
von Anwendungen.
USB MIDI OUT – Sendet
MIDI-Daten an Anwendungen.
(2) MIDI IN – Diese 5-polige DIN-
Buchse empfängt die MIDI-Daten
einer externen Quelle, zum
Beispiel MIDI Keyboard, externer
Hardware Sequencer, Computer
mit MIDI Interface etc.
(3) MIDI THRU – Diese 5-polige
DIN-Buchse leitet die über MIDI
IN empfangenen Daten weiter.
Die Daten werden meistens
zu einem zweiten MODEL D
Synthesizer für den Betrieb
einer Poly Chain oder zu einer
Drum Machine übertragen,
die einem anderen MIDI-Kanal
zugewiesen ist.
Controller-Sektion
(4) OSC3/FILTER EG – Schaltet
zwischen OSC3 und Filter Envelope
als Modulationsquelle um.
(5) GLIDE – Regelt die Stärke des
Glide-Eekts (Portamento)
zwischen den auf der Tastatur
gespielten Noten.
(6) TUNE – Regelt die Frequenz
der Oszillatoren 1, 2 und 3.
(OSC3 bleibt unbeeinusst,
wenn der OSC3 CONTROL-Schalter
auf FILTER EG steht.)
(7) OSCILLATOR MODULATION –
In der Stellung ON werden
die drei Oszillatoren von
der Modulationsmischung
moduliert, die man mit dem MOD
MIX-Regler einstellt.
(8) MOD MIX – Regelt die
Modulationsmischung zwischen
OSC3/Filter EG und Noise/LFO.
(9) NOISE (MOD SRC)/ LFO – Schaltet
zwischen Noise (oder externer
Modulationsquelle) und Low
Frequency Oscillator (LFO) als
Modulationsquelle um.
(10) MOD DEPTH – Regelt die
Modulationsstärke von Null
bis Maximum. Man kann die
Modulationsstärke auch mit
dem Modulationsrad eines MIDI
Keyboards steuern.
(11) WAVE SHAPE – Wählt als
LFO-Wellenform entweder
Dreieck oder Rechteck.
(12) LFO RATE – Regelt die
LFO-Frequenz.
Oscillator Bank-Sektion
(13) OSC 3 CONTROL – Bei aktiviertem
Schalter (ON) variiert die Frequenz
von OSC 3 entsprechend der
Tastaturposition der Noten.
In der Stellung OFF wirken Tastatur,
Pitch-und Modulationsrad nicht
auf OSC 3.
(14) FREQUENCY RANGE – Wählt
einen von 6 Frequenzbereichen
für Oszillator 1, 2 oder 3.
(15) FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENT –
Regelt die Frequenz von Oszillator
2 oder 3.
(16) WAVE SHAPE – Wählt eine
Wellenform für Oszillator 1, 2
oder 3 aus den Optionen: Dreieck,
Dreieck / Sägezahn (OSC1 und 2),
umgekehrter Sägezahn (OSC3),
Sägezahn, Rechteck, medium Puls
und schmaler Puls.
(17) MOD SOURCE (INPUT) – Zum
Anschließen einer externen
Modulationsquelle. Wenn die
Buchse nicht belegt ist, kann man
den internen Noise-Generator als
Modulationsquelle nutzen.
(18) OSC 1V/OCT (INPUT) –
Über diesen Eingang kann
man die Frequenz der 3
Oszillatoren mit einer externen
Steuerspannung regeln (steigt die
Eingangsspannung um 1 Volt an,
erhöht sich die Frequenz um
1 Oktave).
(19) LFO CV (INPUT) – Über diesen
Eingang kann man die LFO-
Frequenz mit einer externen
Steuerspannung regeln.
Mixer-Sektion
(20) VOLUME – Regelt die Lautstärke
von Oszillator 1, 2 oder 3.
(21) ON/OFF – Wählt, welche der
Quellen OSC1, OSC2, OSC3, Noise
und External Input oder eine
beliebige Kombination dieser 5
Quellen gespielt werden soll.
(22) NOISE VOLUME – Regelt die
Lautstärke der internen Noise-
Quelle (Rauschgenerator).
(23) WHITE/PINK – Schaltet die
interne Noise-Quelle zwischen
Pink (Rosa Rauschen) und White
(Weißes Rauschen) um.
(24) OVERLOAD – Zeigt an, wenn die
Audiopegel der Mischung die
Mixer-Sektion übersteuern.
(25) EXT IN VOLUME – regelt den
Pegel von externen Quellen, die in
den externen Eingang eingespeist
werden. Wenn keine Quelle an den
externen Eingang angeschlossen
ist, wird anstelle des externen
Audiomaterials automatisch
der Hauptausgang des MODEL D
hier angeschlossen.
Dies erzeugt einen Feedback-
Signalweg vom Ausgang zurück
zur Mixersektion, mit dem man
extra fette Bässe oder extra Crunch
erzeugen kann. In diesem Fall
steuert der EXT IN Volume-Regler
den Pegel des eingehenden Haupt-
Audiosignals, das zur Mixersektion
zurückgeführt wird.
(26) LFO Triangular (OUTPUT) – Gibt
die interne LFO Dreieck-Welle aus.
(27) LFO Square (OUTPUT) – Gibt die
interne LFO Rechteck-Welle aus.
(28) EXT (INPUT) – An diesen
3,5 mm-Eingang kann man jede
externe Audioquelle mit Line-
Pegel anschließen. Wenn diese
Buchse nicht belegt ist, ist hier
intern der Haupt-Audioausgang
angeschlossen.
(29) MIX (OUTPUT) – Gibt die
endgültige Mischung dieser
Mixer-Sektion aus.
Modiers-Sektion
(30) DECAY – In der Stellung ON
klingt das Signal in der mit dem
DECAY TIME-Regler eingestellten
Zeitspanne aus, nachdem eine
Note oder ein externer Trigger
beendet wurde. In der Stellung
OFF klingt das Signal sofort aus,
nachdem eine Note oder ein
externer Trigger beendet wurde.
LOUDNESS DECAY – Wirkt auf das
Decay des Lautstärkepegels der
Loudness-Sektion.
FILTER DECAY – Wirkt auf das
Decay der Cuto-Frequenz der
Filter-Sektion.
(31) KEYBOARD CONTROL – Diese
Schalter variieren die Wirkung
des Keyboard Tracking, bei dem
das Filter von der Tonhöhe der
gespielten Note beeinusst wird.
Schalter 1 und 2 auf OFF – kein
Keyboard Tracking
Schalter 1 und 2 auf ON –
maximale Wirkung
nur Schalter 1 auf ON – ⁄ der
maximalen Wirkung
nur Schalter 2 auf ON – ⁄ der
maximalen Wirkung
(32) FILTER MODULATION – In der
Stellung ON wird die Filter-Sektion
vom Modulation Mix moduliert,
der mit dem MOD MIX-Regler
eingestellt wurde.
(33) FILTER MODE – Wählt zwischen
Low-Pass-und High-Pass-Filter.
(34) LOUDNESS CONTOUR –
Diese 3 Regler steuern die
gesamte Hüllkurve des Audios,
nachdem es die Mixer-und
Filter-Sektion durchlaufen hat.
Die Regler beeinussen die
Lautstärkeänderung (Loudness)
im Zeitverlauf.
ATTACK – Regelt die Zeitspanne,
in der ein Signal nach dem
Anschlagen einer Note seinen
Maximalpegel erreicht.
DECAY TIME – Regelt die
Zeitspanne, in der ein Signal
nach Ablauf der Attack-Zeit
auf den Sustain-Pegel abfällt.
Wenn der LOUDNESS DECAY-
Schalter auf ON steht, ist dies auch
die Zeitspanne, in der das Signal
nach Loslassen der Taste auf den
Minimalpegel abfällt.
SUSTAIN – Regelt den
Lautstärkepegel, auf dem das
Signal ausgehalten wird, nachdem
die Attack-Zeit und anfängliche
Decay-Zeit abgelaufen sind.
(35) FILTER ENVELOPE CONTROLS –
Diese 3 Regler steuern die gesamte
Hüllkurve der Filtersektion. Die
Regler wirken auf die Änderung
der Cuto-Frequenz im Zeitverlauf.
ATTACK – Regelt die Zeitspanne,
in der die Cuto-Frequenz von
ihrem eingestellten Wert auf die
Frequenz ansteigt, die mit dem
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR-Regler
eingestellt ist.
DECAY TIME – Regelt die
Zeitspanne, in der die Cuto-
Frequenz nach Ablauf der
Attack-Zeit auf die Sustain-
Frequenz abfällt. In der Stellung
ON des FILTER DECAY-Schalters
regelt diese Decay-Zeit auch, wie
schnell die Cuto-Frequenz von
der Sustain-Frequenz abfällt,
nachdem ein Note beendet wurde.
SUSTAIN – Bestimmt die
Cuto-Frequenz, die nach Ablauf
der Attack-Zeit und anfänglichen
Decay-Zeit beibehalten wird.
(36) FILTER CONTROLS – Mit dem
FILTER MODE-Schalter kann man
ein Low-Pass-oder High-Pass-
Filter wählen. Im Low-Pass-Modus
werden Audiofrequenzen über
der Cuto-Frequenz bedämpft.
Im High-Pass-Modus werden
Audiofrequenzen unter der
Cuto-Frequenz bedämpft.
CUTOFF FREQUENCY – Bestimmt
die Cuto-Frequenz des Filters.
FILTER EMPHASIS – Bestimmt,
wie stark die Lautstärke an der
Cuto-Frequenz angehoben
wird (Resonance).
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR
– Bestimmt die Stärke der
Frequenzverschiebung, die auf die
Cuto-Frequenz angewandt wird.
(37) CUT CV (INPUT) – Zum
Anschließen einer
Steuerspannung zur Steuerung
der Cuto-Frequenz.
(38) FC GATE (INPUT) – Zum
Anschließen einer externen
Trigger-Spannung zum Triggern
der Filterkontur.
(39) FILT CONT (OUTPUT) – Zur
Ausgabe der Filterkontur.
(40) LC GATE (INPUT) – Zum
Anschließen einer externen
Trigger-Spannung zum Triggern
der Lautstärkekontur.
(41) LOUD CONTOUR (OUTPUT) – Zur
Ausgabe der Lautstärkekontur.

34 35Quick Start GuideMODEL D
Output-Sektion
(42) A-440 – Hier schaltet man
die Ausgabe eines 440 Hz
Kammertons zum Stimmen von
Instrumenten ein. Mit diesem
Schalter kann man beim
Einschalten des Geräts auch
in verschiedene Betriebsarten
wechseln (nähere Einzelheiten
im Abschnitt „Erste Schritte“
dieses Handbuchs).
(43) POWER – Diese LED leuchtet,
wenn der Synthesizer ans
Stromnetz angeschlossen und
eingeschaltet ist.
(44) VOLUME – Regelt die
Gesamtlautstärke des
Synthesizer-Ausgangssignals.
(45) VOLUME (KOPFHÖRER) – Regelt
die Gesamtlautstärke des
PHONES-Ausgangs.
(46) PHONES – An diesen 3,5 mm
TRS-Ausgang schließt man
Kopfhörer an. Drehen Sie die
Kopfhörer-Lautstärke zurück,
bevor Sie die Kopfhörer aufsetzen.
(47) ON – Damit kann man den Haupt-
Audioausgang des Synthesizers
schnell ein-oder stummschalten.
(48) LOUD CV (INPUT) – Zum
Anschließen einer externen
Steuerspannung zur Steuerung
der Lautstärkekontur.
(49) MAIN (OUTPUT) – Über diesen
3,5 mm TRS-Anschluss wird das
Hauptaudiosignal ausgegeben.
Er wird normalerweise mit dem
Audioeingang des MODEL D oder
den Audioeingängen anderer
modularer Synthesizer
verbunden. Beim Betrieb des
MODEL D in einem Eurorack ist
dies der Hauptausgang, da die
rückseitigen Ausgänge nicht
verwendet werden.
Rückseite
(50) MAIN OUTPUT
– Verbinden Sie
diese 6,3 mm TRS-Ausgänge
wie folgt mit den Eingängen
externer Geräte (Hinweis: Dies
sind keine Links-Rechts-Ausgänge,
sondern zwei Mono-Ausgänge):
LOW – Diesen Mono-Ausgang
mit Instrumentenpegel kann
man beispielsweise an Eingänge
mit Instrumentenpegel von
Gitarrenverstärkern oder
Mixern anschließen.
HIGH – Diesen Mono-Ausgang
mit Line-Pegel kann man
beispielsweise an Eingänge
mit Line-Pegel von Mixern,
Keyboard-Verstärkern oder
Aktivlautsprechern anschließen.
(51) MIDI CHANNEL
– Mit diesen
4 Schaltern kann man eine
MIDI-Kanalnummer von 1 bis
16 einstellen (siehe Tabelle
auf Seite 15). Man kann den
MIDI-Kanal auch mit MIDI
SysEx-Befehlen ändern (siehe
MIDI SysEx-Tabellen weiter
unten). (Diese Methode wird
verwendet, wenn der MODEL D
in einem Eurorack installiert ist
und diese Schalter nicht mehr
vorhanden sind.)
(52) POWER
– Schaltet den Synthesizer
ein oder aus. Stellen Sie vor
dem Einschalten alle nötigen
Anschlüsse her und drehen Sie
die Lautstärke zurück.
(53) DC INPUT – Hier schließt man den
mitgelieferten 12V DC Netzadapter
an. Man kann den Netzadapter mit
einer Netztsteckdose verbinden,
die 100 V bis 240 V Spannung bei
50 Hz/60 Hz liefert. Verwenden
Sie nur den mitgelieferten
Netzadapter.
(DE) Schritt 2: Bedienelemente (PT) Passo 2: Controles
Seção MIDI
(1) USB PORT – Essa tomada USB
do tipo B possibilita conexão
a um computador. O MODEL D
aparecerá como um dispositivo
compatível com a classe USB MIDI,
capaz de suportar entrada e
saída MIDI.
USB MIDI IN – aceita dados MIDI
provenientes de um aplicativo.
USB MIDI OUT – envia dados MIDI
para um aplicativo.
(2) MIDI IN – Este jack DIN de 5
pinos recebe dados MIDI de uma
fonte externa. Geralmente de um
teclado MIDI, um seqüenciador
de hardware externo, um
computador equipado com
interface MIDI, etc.
(3) MIDI THRU – Este jack DIN de 5
pinos é usado para passar dados
MIDI recebidos no MIDI INPUT.
Isso geralmente é enviado a um
outro sintetizador MODEL D para
rodar um Poly Chain ou caixa de
ritmos designados a um canal
MIDI deferente.
Seção Controladores
(4) OSC3/FILTER EG – comuta entre
OSC3 ou Filter Envelope como uma
fonte de modulação.
(5) GLIDE – ajusta o valor de Glide
(Portamento), entre notas
no teclado.
(6) TUNE – ajusta a freqüência dos
osciladores 1, 2, e 3. (OSC3 não é
afetado se o botão OSC3 CONTROL
estiver desligado .)
(7) OSCILLATOR MODULATION –
quando ligado, os três osciladores
são modulados pelo mix de
modulação, ajustado pelo botão
MOD MIX.
(8) MOD MIX – ajusta a modulação
do mix entre o OSC3/Filter
EG e Noise/LFO.
(9) NOISE (MOD SRC)/ LFO –
comuta entre Ruído (ou fonte de
modulação externa) ou Oscilador
de Baixa Frequência (LFO) como
fonte de modulação.
(10) MOD DEPTH – ajusta a
profundidade da modulação
variando de desligada até o
valor máximo. A profundidade
da modulação também pode
ser ajustada usando o botão de
modulação no teclado MIDI.
(11) WAVE SHAPE – selecione o
formato da onda LFO (oscilador
de baixa freqüência) ou da onda
triangular ou quadrada.
(12) LFO RATE – ajusta a frequência
de LFO.
Seção Banco de Oscilador
(13) OSC 3 CONTROL – quando ligado,
a frequência do OSC 3 varia de
acordo com o teclado. Quando
desligado, o teclado, botão de
tons, e botão de modulação não
terão efeito algum no OSC 3.
(14) FREQUENCY RANGE – selecione
uma das seis frequências do
Oscilador 1, 2, ou 3.
(15) FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENT –
ajusta a frequência do Oscilador
2 ou 3.
(16) WAVE SHAPE – seleciona o
formato da onda do Oscilador
1, 2, ou 3 a partir de: triangular,
triangular/ dente de serra (OSC1 e
2), dente de serra invertida (OSC3),
dente de serra, quadrada, pulso
médio, e pulso estreito.
(17) MOD SOURCE (INPUT) – permite
conexão de uma fonte de
modulação externa. Se nada
estiver conectado aqui, então a
gerador de ruído interno estará
disponível como uma fonte
de modulação.
(18) OSC 1V/OCT (INPUT) – esta
entrada permite que a frequência
dos três osciladores seja ajustada
por um controle de voltagem
externo (a entrada de 1 Volt
aumentará a frequência em
u tava.
(19) LFO CV (INPUT) – permite
controle da frequência LFO por um
controle de voltagem externo.
Seção Mixer
(20) VOLUME – ajusta o volume do
Oscilador 1, 2, ou 3.
(21) ON/OFF – seleciona as fontes para
reprodução a partir de OSC1, OSC2,
OSC3, Ruído, e Entrada Externa,
ou qualquer combinação dessas
5 fontes.
(22) NOISE VOLUME – ajusta o nível da
fonte de ruído interna.
(23) WHITE/PINK – comuta a fonte de
ruído interna de ruído rosa para
ruído branco.
(24) OVERLOAD – indica quando os
níveis de áudio da mixagem estão
sobrecarregando a seção mixer.
(25) EXT IN VOLUME – ajuste o
nível de qualquer fonte externa
reproduzindo para a entrada
externa. Se nada estiver conectado
à entrada externa, então em
vez de se ter qualquer áudio
externo entrando neste ponto,
a saída principal MODEL D será
automaticamente conectada aqui.
Isto cria um caminho de feedback
proveniente da saída de volta para
a seção mixer que oferece um som
grave mais encorpado ou mais cru.
Neste caso, o controle de volume
EXT IN ajustará o nível do áudio
principal de entrada alimentado
de volta à seção mixer.
(26) LFO Triangular (OUTPUT) – faz
a saída do sinal de onda triangular
LFO interno.
(27) LFO Square (OUTPUT) – faz a
saída do sinal de onda quadrado
LFO interno.
(28) EXT (INPUT) – conecta qualquer
fonte de áudio de nível de linha
externa a esta entrada de 3.5 mm.
Se nada estiver conectado ali,
então a saída de áudio principal
está internamente conectada a
essa entrada externa.
(29) MIX (OUTPUT) – faz a saída do
mix nal desta seção Mixer.

36 37Quick Start GuideMODEL D
(PT) Passo 2: Controles
Seção Modicadores
(30) DECAY – quando ligado, o sinal
decai durante o tempo ajustado
pelo botão DECAY TIME depois que
uma nota ou acionador externo
é solta. Quando desligado, decai
imediatamente depois que uma
nota ou acionador externo é solta.
LOUDNESS DECAY – afeta o
decaimento do nível de volume da
seção de sonoridade Loudness.
FILTER DECAY – afeta o
decaimento da frequência de corte
na seção ltro.
(31) KEYBOARD CONTROL – esses
controles variam o efeito de
tracking do teclado, onde a
seção ltro é afetada pelo tom da
nota tocada.
Botão 1 e 2 OFF – sem efeito
tracking do teclado.
Botão 1 e 2 ON – efeito máximo
Botão 1 ON (apenas) – ⁄ do
efeito máximo
Botão 2 ON (apenas) – ⁄ do
efeito máximo
(32) FILTER MODULATION – quando
ligada, a seção do ltro é
modulada pelo mix de modulação,
ajustado pelo botão MOD MIX.
(33) FILTER MODE – seleciona o ltro
entre Passa Baixa ou Passa Alta.
(34) LOUDNESS CONTOUR – esses 3
botões ajustam o formato geral
fazendo o envelope do áudio
depois de ter passado pela seção
mixer e lter. Os controles afetam
a mudança em nível de volume
(sonoridade) com o tempo.
ATTACK – ajusta o tempo que
leva para o sinal alcançar um
nível máximo depois que a nota
é tocada.
DECAY TIME – ajusta o tempo
que leva para um sinal decair até
o nível de volume de sustentação
depois do tempo de ataque
ter acabado. Se o botão LOUDNESS
DECAY estiver ligado, também
signica quanto tempo levará para
decair até o mínimo após uma
nota ser solta.
SUSTAIN – ajusta o nível do
volume com o qual o sinal é
sustentado depois que o tempo
de ataque e decaimento inicial
tiverem sido alcançados.
(35) FILTER ENVELOPE CONTROLS –
esses 3 botões ajustam o formato
geral que faz o envelope da seção
do ltro. Os controles afetam a
mudança em frequência de corte
com o tempo.
ATTACK – ajusta o tempo para a
frequência de corte aumentar o
seu valor congurado e chegar à
frequência ajustada pelo controle
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR.
DECAY TIME – ajusta o tempo
para a frequência de corte
decair até chegar à frequência
de sustentação após o tempo
de ataque ter terminado.
Se o botão FILTER DECAY estiver
ligado, então este tempo de
decaimento também será o tempo
que leva para o decaimento
acontecer a partir da frequência
de sustentação quando uma
nota for solta.
SUSTAIN – ajusta o corte de uma
frequência que é sustentada após
o tempo de ataque e decaimento
inicial terem sido alcançados.
(36) FILTER CONTROLS – o ltro
pode ser Low-Pass (passa baixa)
ou High-Pass (passa alta),
dependendo da conguração
do botão FILTER MODE. Em
modo Low-Pass, frequências de
áudio acima da frequência de
corte são atenuadas. No modo
High-Pass, frequências de áudio
abaixo da frequência de corte
são atenuadas.
CUTOFF FREQUENCY – ajusta a
frequência de corte do ltro.
FILTER EMPHASIS – ajusta a
quantidade de aumento do nível
de volume (ressonância) dado na
frequência de corte.
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR – ajusta
a quantidade da mudança de
frequência dado à frequência
de corte.
(37) CUT CV (INPUT) – permite
conexão de voltagem de controle
para controlar a frequência
de corte.
(38) FC GATE (INPUT) – permite que
uma voltagem acionadora externa
seja aplicada para acionar a curva
de ltro.
(39) FILT CONT (OUTPUT) – faz a saída
da curva de ltro.
(40) LC GATE (INPUT) – permite que
uma voltagem acionadora externa
seja aplicada para acionar as
curvas sonoras.
(41) LOUD CONTOUR (OUTPUT) – faz a
saída das curvas sonoras.
Seção Output
(42) A-440 – use-o para ligar um sinal
de sintonia de saída de intervalo
de 440 Hz. Este botão também
pode ser usado para entrar em
modos variados enquanto ligado
(vericar a seção Primeiros
Passos deste manual para obter
mais detalhes).
(43) POWER – este LED mostra quando
a alimentação é aplicada e o
sintetizador está ligado.
(44) VOLUME – ajusta o nível
de volume geral da saída
do sintetizador.
(45) VOLUME (HEADPHONE) – ajusta
o nível de volume geral da
saída PHONES.
(46) PHONES – conecte seus fones de
ouvido a esta saída TRS de 3.5 mm.
Verique se o volume dos fones
de ouvido está abaixado antes de
colocar os fones de ouvido.
(47) ON – use para ligar rapidamente
ou colocar a saída de áudio
principal do sintetizador em
modo mute.
(48) LOUD CV (INPUT) – permite
conexão de uma voltagem de
controle externa para controlar as
curvas de sonoridade.
(49) MAIN (OUTPUT) – use esta
conexão TRS de 3.5 mm como
saída principal de áudio.
Geralmente, há um patch entre
ela e a entrada de áudio do
MODEL D ou a entrada de áudio de
outro equipamento sintetizador
modular. Se estiver usando um
MODEL D em um Eurorack, então
esta é a saída principal, pois os
conectores de saída do painel
traseiro não são usados.
Painel Traseiro
(50) MAIN OUTPUT – conecte essas
saídas TRS de ¼" às entradas
do seu equipamento externo
da seguinte maneira (observe
que são ambos Mono, e não
esquerda/direita):
LOW – esta saída mono de nível de
instrumento pode ser conectada às
entradas de nível de instrumento
de amplicadores de guitarra ou
misturadores, por exemplo.
HIGH – esta saída mono de nível
de linha pode ser conectada a
entradas de nível de linha de
misturadores, amplicadores
de teclados, ou alto-falantes
alimentados, por exemplo.
(51) MIDI CHANNEL – estes 4 botões
permitem ajustar o número do
canal MIDI de 1 a 16 (vericar
tabela na página 15). O canal MIDI
também pode ser mudado usando
os comandos MIDI SysEx, conforme
demonstrado nas tabelas MIDI
SysEx mais adiante neste manual.
(Este método é usado quando o
MODEL D está instalado em um
Eurorack, e esses botões não estão
mais presentes.)
(52) POWER – liga ou desliga o
sintetizador. Verique se todas
as conexões foram feitas, e se o
volume está abaixado antes de
ligar a unidade.
(53) DC INPUT – conecte o adaptador
DC de 12V aqui. A alimentação
do adaptador pode ser ligada
a uma tomada AC capaz de
fornecer de 100V até 240V a 50
Hz/60 Hz. Use apenas com o
adaptador fornecido.

38 39Quick Start GuideMODEL D
(IT) Passo 2: Controlli
Sezione MIDI
(1) USB PORT – Questa presa USB di
tipo B consente il collegamento
a un computer. Il MODELLO D
apparirà come un dispositivo MIDI
USB conforme alla classe, in grado
di supportare MIDI in e out.
USB MIDI IN – accetta dati MIDI
in ingresso da un’applicazione.
USB MIDI OUT – invia dati MIDI
a un’applicazione.
(2) MIDI IN – questo jack DIN a
5 pin riceve i dati MIDI da una
sorgente esterna. Questa sarà
comunemente una tastiera
MIDI, un sequencer hardware
esterno, un computer dotato di
un’interfaccia MIDI, ecc.
(3) MIDI THRU – questa presa DIN a 5
pin viene utilizzata per far passare
i dati MIDI ricevuti al MIDI INPUT.
Questo verrà comunemente inviato
a un altro sintetizzatore MODEL D
per eseguire una Poly Chain o ad
una drum machine assegnata a un
diverso canale MIDI.
Sezione controllori
(4) OSC3 / FILTER EG – cambia tra
OSC 3 o Filter Envelope come
sorgente di modulazione.
(5) GLIDE – regola la quantità
di Glide (Portamento), tra le note
sulla tastiera.
(6) TUNE – regolare la frequenza
degli oscillatori 1, 2 e 3. (OSC3 non
è inuenzato se l’interruttore OSC3
CONTROL è spento.)
(7) OSCILLATOR MODULATION –
quando è ON, i tre oscillatori sono
modulati dal mix di modulazione,
impostato dalla manopola MOD MIX.
(8) MOD MIX – regola il mix di
modulazione tra OSC3 / Filter EG e
Noise / LFO.
(9) NOISE (MOD SRC)/ LFO –
commuta tra Noise (o sorgente di
modulazione esterna) o Oscillatore
a bassa frequenza (LFO) come
sorgente di modulazione.
(10) MOD DEPTH – regolare la
profondità di modulazione da
o al massimo. La profondità di
modulazione può anche essere
regolata utilizzando la rotella di
modulazione su una tastiera MIDI.
(11) WAVE SHAPE – seleziona la forma
d’onda dell’LFO tra triangolare
o quadra.
(12) LFO RATE – regola la frequenza
dell’LFO.
Sezione Oscillator Bank
(13) OSC 3 CONTROL – quando è ON, la
frequenza dell’Oscillatore 3 varierà
con la tastiera. Quando è OFF, la
tastiera, la rotella Pitch e la rotella
Modulation non avranno eetto
su OSC3.
(14) FREQUENCY RANGE – selezionare
tra sei gamme di frequenza
dell’oscillatore 1, 2 o 3.
(15) FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENT
– regolare la frequenza
dell’oscillatore 2 o 3.
(16) WAVE SHAPE – selezionare
la forma d’onda utilizzata per
Oscillatore 1, 2 o 3 tra: triangolare,
triangolare / dente di sega (OSC 1
e 2), dente di sega inverso (OSC 3),
dente di sega, quadrato, impulso
medio e impulso stretto.
(17) MOD SOURCE (INPUT) – consente
il collegamento di una sorgente
di modulazione esterna. Se non è
collegato nulla qui, il generatore di
rumore interno è disponibile come
sorgente di modulazione.
(18) OSC 1V / OCT (INGRESSO) –
questo ingresso permette di
regolare la frequenza dei tre
oscillatori tramite una tensione
di controllo esterna (aumento di
1 Volt in ingresso, aumenterà la
frequenza di un’ottava).
(19) LFO CV (INPUT) – consente il
controllo della frequenza LFO tramite
una tensione di controllo esterna.
Sezione mixer
(20) VOLUME – regolare il volume
dell’oscillatore 1, 2 o 3.
(21) ON/OFF – selezionare le sorgenti
da riprodurre da OSC 1, OSC 2,
OSC 3, Noise e External Input o
qualsiasi combinazione di queste
5 sorgenti.
(22) NOISE VOLUME – regolare il
livello della sorgente di rumore
interna.
(23) WHITE/PINK – cambia la sorgente
di rumore interna da Pink noise a
White noise.
(24) OVERLOAD – indica quando
i livelli audio del mix stanno
sovraccaricando la sezione mixer.
(25) EXT IN VOLUME – Regola il livello
di qualsiasi sorgente esterna
riprodotta nell’ingresso esterno. Se
non è collegato nulla all’ingresso
esterno, invece di qualsiasi audio
esterno in arrivo a questo punto,
l’uscita principale MODEL D viene
automaticamente collegata qui.
Questo crea un percorso di
feedback dall’uscita alla sezione
mixer, per ottenere bassi più
potenti o crunch extra. In questo
caso, il controllo del volume
EXT IN regola il livello dell’audio
principale in ingresso reintrodotto
nella sezione mixer.
(26) LFO Triangular – emette il
segnale a onda triangolare
dell’LFO interno.
(27) LFO Square (OUTPUT) – emette
il segnale a onda quadra dell’LFO
interno.
(28) EXT (INPUT) – collegare qualsiasi
sorgente audio a livello di linea
esterna a questo ingresso da 3,5
mm. Se non è collegato nulla
qui, l’uscita audio principale è
collegata internamente a questo
ingresso esterno.
(29) MIX (USCITA) – emette il mix
nale da questa sezione Mixer.
Sezione Modicatori
(30) DECAY – quando è attivo, il
segnale decade durante il tempo
impostato dalla manopola DECAY
TIME dopo il rilascio di una nota
o di un trigger esterno. Quando
è OFF, decade immediatamente
dopo il rilascio di una nota o di un
trigger esterno.
LOUDNESS DECAY – inuisce sul
decadimento del livello del volume
della sezione Loudness.
FILTER DECAY – inuenza il
decadimento della frequenza di
taglio della sezione Filter.
(31) KEYBOARD CONTROL – questi
interruttori variano l’eetto del
tracciamento della tastiera, dove
la sezione del ltro è inuenzata
dall’intonazione della nota suonata.
Switch 1 e 2 su OFF – nessun
eetto di tracciamento della tastiera
Switch 1 e 2 su ON –
massimo eetto
Switch 1 ON (solo) –
⁄ dell’eetto massimo
Switch 2 ON (solo) –
⁄ dell’eetto massimo
(32) FILTER MODULATION – quando è
ON, la sezione del ltro è modulata
dal mix di modulazione, impostato
dalla manopola MOD MIX.
(33) FILTER MODE – seleziona il ltro
tra passa basso o passa alto.
(34) LOUDNESS CONTOUR – queste
3 manopole regolano la forma
complessiva che avvolge l’audio
dopo che è passato attraverso la
sezione mixer e la sezione ltri. I
controlli inuenzano la variazione
del livello di volume (loudness)
nel tempo.
ATTACK – regola il tempo
impiegato dal segnale per
raggiungere un livello massimo
dopo che una nota è stata suonata.
DECAY TIME – regola il tempo di
decadimento di un segnale no
al livello di volume di sostegno
dopo che il tempo di attacco
è terminato. Se l’interruttore
LOUDNESS DECAY è su ON, questo
è anche il tempo necessario per
decadere al minimo una volta
rilasciata una nota.
SUSTAIN – Regola il livello di
volume a cui il segnale viene
sostenuto dopo che il tempo di
attacco e il tempo di decadimento
iniziale sono stati raggiunti.
(35) FILTER ENVELOPE CONTROLS
– queste 3 manopole regolano la
forma complessiva che avvolge
la sezione del ltro. I controlli
inuenzano la variazione della
frequenza di taglio nel tempo.
ATTACK – Regolare il tempo per la
frequenza di taglio per aumentare
dal suo valore impostato e
raggiungere la frequenza impostata
dal controllo AMOUNT OF CONTOUR.
DECAY TIME – Regola il tempo per
il decadimento della frequenza di
taglio no alla frequenza di sustain
dopo che il tempo di attacco è
terminato. Se l’interruttore FILTER
DECAY è su ON, questo tempo di
decadimento è anche il tempo
necessario per decadere dalla
frequenza di sustain una volta
rilasciata una nota.
SUSTAIN – Regola il taglio su una
frequenza che viene sostenuta
dopo che il tempo di attacco e il
tempo di decadimento iniziale
sono stati raggiunti.
(36) FILTER CONTROLS – il ltro può
essere passa-basso o passa-alto,
a seconda dell’impostazione
dell’interruttore FILTER MODE. In
modalità passa-basso, le frequenze
audio al di sopra della frequenza
di taglio vengono attenuate. In
modalità passa-alto, le frequenze
audio al di sotto della frequenza di
taglio vengono attenuate.
CUTOFF FREQUENCY – regola la
frequenza di taglio del ltro.
FILTER EMPHASIS – regola la
quantità di aumento del livello
di volume (risonanza) dato alla
frequenza di taglio.
AMOUNT OF CONTOUR – regola
la quantità di spostamento di
frequenza dato alla frequenza
di taglio.
(37) CUT CV (INPUT) – consente il
collegamento di una tensione
di controllo per controllare la
frequenza di taglio.
(38) FC GATE (INGRESSO) – consente
di applicare una tensione di trigger
esterno per attivare il contorno
del ltro.
(39) FILT CONT (USCITA) – emette il
contorno del ltro.
(40) LC GATE (INGRESSO) – consente
di applicare una tensione di trigger
esterno per attivare il contorno
del volume.
(41) LOUD CONTOUR – emette il
prolo del volume.
Sezione di output
(42) A-440 – usalo per attivare un
segnale di accordatura in uscita di
altezza concerto 440 Hz. Questo
interruttore può essere utilizzato
anche per accedere a varie modalità
durante l’accensione (vedere la
sezione Guida introduttiva di questo
manuale per maggiori dettagli).
(43) POWER – questo LED mostra
quando l’alimentazione è applicata
e il sintetizzatore è acceso.
(44) VOLUME – regola il livello di
volume generale dell’uscita del
sintetizzatore.
(45) VOLUME (CUFFIE) – regola
il livello di volume generale
dell’uscita PHONES.
(46) PHONES – collega le tue cue
a questa uscita TRS da 3,5 mm.
Assicurati che il volume delle cue
sia abbassato prima di indossare
le cue.
(47) ON – usalo per attivare o
disattivare rapidamente l’uscita
audio principale del sintetizzatore.
(48) LOUD CV – consente il
collegamento di una tensione di
controllo esterna per controllare il
Loudness Contour.
(49) MAIN (USCITA) – utilizzare
questa connessione TRS da 3,5
mm per emettere l’uscita audio
principale. Tipicamente è collegato
a un ingresso audio del MODELLO
D o agli ingressi audio di altre
apparecchiature di sintetizzatore
modulare. Se si utilizza il MODELLO
D in un Eurorack, questa è l’uscita
principale, poiché i connettori di
uscita del pannello posteriore non
vengono utilizzati.
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
Strona się ładuje...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
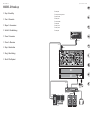 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
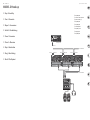 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
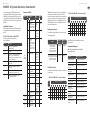 35
35
-
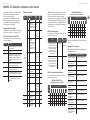 36
36
-
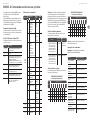 37
37
-
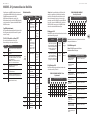 38
38
-
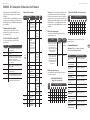 39
39
-
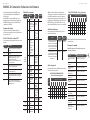 40
40
-
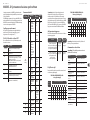 41
41
-
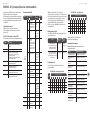 42
42
-
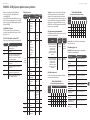 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
Behringer Model D Skrócona instrukcja obsługi
- Kategoria
- Klawiatury MIDI
- Typ
- Skrócona instrukcja obsługi
w innych językach
- español: Behringer Model D Guía de inicio rápido
- italiano: Behringer Model D Guida Rapida
- Deutsch: Behringer Model D Schnellstartanleitung
- português: Behringer Model D Guia rápido
- français: Behringer Model D Guide de démarrage rapide
- Nederlands: Behringer Model D Snelstartgids

























































